How To Protect Yourself From Fraud In Metaverse: Types Of Frauds In Metaverse

The concept of the metaverse has gained significant attention and popularity in recent years, especially in the fields of technology, gaming, and virtual reality. The metaverse refers to a virtual universe or a collective virtual shared space where people can interact with one another and digital entities in real-time, using virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), or other immersive technologies.
In simple terms, the metaverse is a digital extension of the physical world that allows users to engage with a computer-generated environment and interact with other users in a manner that feels natural and lifelike. It is a fully realized, immersive virtual space that encompasses various forms of media, including 3D graphics, audio, video, and even haptic feedback (physical sensations).
The metaverse is not just limited to a single platform or application. It is an interconnected network of virtual worlds, spaces, and experiences that span across different devices, platforms, and technologies. Users can access the metaverse through devices such as VR headsets, smartphones, tablets, and computers, and they can seamlessly transition between different virtual environments.
In the metaverse, users can create avatars, digital representations of themselves, which they can customize and control within the virtual space. These avatars allow individuals to navigate and explore the metaverse, interact with other users, participate in activities, and experience a wide range of digital content and services.
The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. It can offer new avenues for social interaction, entertainment, education, commerce, and much more. People can gather in virtual spaces to attend events, concerts, conferences, or engage in collaborative work. It can also enable immersive gaming experiences, where players can explore vast virtual worlds, compete with others, and embark on epic adventures.
The metaverse also has significant implications for business and the economy. It can provide a platform for virtual commerce, where users can buy and sell virtual goods, services, and assets, using digital currencies. Brands and businesses can establish a virtual presence, engage with customers, and offer unique experiences and products within the metaverse. Moreover, the metaverse can enable new forms of advertising and marketing, leveraging immersive and interactive techniques to reach audiences.
However, the concept of the metaverse is still evolving, and its full realization is yet to be achieved. Currently, various companies and organizations are working on developing the infrastructure, technologies, and standards required for a seamless and interconnected metaverse experience. These efforts involve advancements in areas such as virtual reality, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing.
While the metaverse holds tremendous potential, it also raises important considerations related to privacy, security, ethics, and access. Ensuring that the metaverse is inclusive, equitable, and respects user rights and freedoms will be crucial as it continues to develop.
The metaverse represents a vision of a fully immersive and interconnected virtual universe where people can live, work, and play. It promises to redefine how we interact with digital content, collaborate with others, and experience the world around us. As technology progresses and innovation continues, the metaverse has the potential to become an integral part of our everyday lives, transforming the way we connect, communicate, and engage with the digital realm.
Importance of Metaverse for the economy
The metaverse holds significant importance for the economy due to its potential to create new opportunities, reshape industries, and drive economic growth. Here are several reasons why the metaverse is important for the economy:
1. Virtual Commerce: The metaverse provides a platform for virtual commerce, allowing users to buy and sell digital goods, services, and assets using digital currencies. This opens up new revenue streams for businesses and individuals. Companies can create and sell virtual products, such as virtual real estate, virtual fashion, or virtual art. The metaverse enables unique shopping experiences and new business models, driving economic activity and generating jobs.
2. Enhanced Advertising and Marketing: The metaverse introduces innovative advertising and marketing opportunities. Brands can establish a virtual presence within the metaverse, engaging with users in immersive and interactive ways. Advertisers can leverage personalized and targeted advertising techniques, leveraging user data and preferences to deliver more relevant and engaging experiences. This creates new avenues for revenue generation and allows businesses to reach audiences in novel ways.
3. Job Creation: The development and operation of the metaverse require a diverse range of skills and expertise. As the metaverse expands, it will create job opportunities in various fields, including software development, virtual world design, 3D modeling, virtual economy management, content creation, community management, and more. This can stimulate employment and economic growth, especially in the technology and creative sectors.
4. Virtual Events and Conferences: The metaverse offers the potential to host virtual events, conferences, and exhibitions. This opens up new possibilities for businesses and organizations to connect with a global audience without the limitations of physical space and logistics. Virtual events can attract participants from around the world, reduce costs, and provide unique interactive experiences. This benefits not only event organizers but also the hospitality, tourism, and entertainment industries.
5. Collaboration and Remote Work: The metaverse can facilitate collaboration and remote work on a whole new level. Teams can gather in virtual environments, work on projects together, and communicate seamlessly regardless of geographical distances. This can increase productivity, reduce travel costs, and enable a more flexible and inclusive work environment. The metaverse has the potential to reshape the future of work and transform traditional office spaces.
6. Economic Inclusion: The metaverse has the potential to bridge the digital divide and promote economic inclusion. It can provide opportunities for individuals in regions with limited access to physical infrastructure or traditional job markets. Users can participate in the virtual economy, create and monetize content, and engage in entrepreneurship within the metaverse. This can empower individuals and communities, fostering economic growth and reducing inequality.
7. Innovation and Technological Advancements: The development of the metaverse requires advancements in various technologies, including virtual reality, augmented reality, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cloud computing. These technological advancements have broader implications beyond the metaverse itself. They can drive innovation in multiple industries, leading to the creation of new products, services, and business models. This fuels economic growth, fosters competitiveness, and positions countries and companies at the forefront of technological advancements.
The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize the economy by creating new economic opportunities, transforming industries, and driving innovation. It offers virtual commerce, enhanced advertising and marketing, job creation, virtual events and conferences, collaboration and remote work capabilities, economic inclusion, and technological advancements. As the metaverse continues to evolve, its economic impact is expected to grow, shaping the way businesses operate and interact with consumers in the digital realm.
Risks of fraud in the Metaverse
The Metaverse is a virtual reality space where users can interact with each other and digital objects in a simulated environment. While the concept of the Metaverse holds immense potential for social interactions, entertainment, and commerce, it also presents various risks, including the potential for fraud. Here are some of the key risks associated with fraud in the Metaverse:
1. Identity theft: In the Metaverse, users create digital identities or avatars to represent themselves. These avatars may have virtual assets, currencies, and personal information associated with them. Just like in the real world, identity theft can occur in the Metaverse, where malicious actors may try to steal or impersonate someone’s avatar, gaining unauthorized access to their assets and personal information.
2. Phishing and scams: Phishing attacks and scams are common in the digital realm, and the Metaverse is no exception. Fraudsters may create virtual environments, websites, or applications that mimic legitimate platforms to trick users into revealing their login credentials, financial information, or other sensitive data. They can use this information to gain unauthorized access to user accounts and carry out fraudulent activities.
3. Virtual asset theft: The Metaverse often involves the ownership and trading of virtual assets, including digital currencies, virtual real estate, virtual items, and more. Just like physical property theft, virtual asset theft is a risk in the Metaverse. Hackers or fraudsters may exploit vulnerabilities in the Metaverse infrastructure, user accounts, or virtual wallets to steal valuable virtual assets from users.
4. Ponzi schemes and investment fraud: The Metaverse has its own economy, with virtual currencies and virtual marketplaces. Fraudsters may take advantage of this by promoting Ponzi schemes or investment opportunities that promise high returns. They may lure users into investing their real or virtual currency, only to disappear with the funds or manipulate the virtual economy to their advantage.
5. Counterfeit goods and services: The Metaverse allows for the creation and sale of digital goods and services. However, this also opens up the possibility of counterfeit goods or services being sold. Fraudsters can create fake virtual items or offer services that they have no intention of delivering, thereby defrauding unsuspecting users.
6. Malware and hacking: The Metaverse relies on various technologies and platforms to operate. Malware and hacking attacks can compromise the security of these platforms, potentially leading to unauthorized access to user accounts, theft of personal information, or disruption of the Metaverse experience. Malicious actors may exploit vulnerabilities in the Metaverse software or use social engineering techniques to trick users into downloading and installing malware.
7. Virtual currency fraud: Virtual currencies, such as cryptocurrencies or in-game currencies, are often used in the Metaverse for transactions and purchases. Fraudsters may create fake virtual currencies or manipulate the value of existing ones to deceive users. They may entice users to invest in or purchase virtual currencies that have no real value or credibility.
8. Account hijacking: Metaverse platforms typically require user accounts for access and interaction. Account hijacking occurs when fraudsters gain unauthorized access to user accounts through various means, such as phishing, brute-force attacks, or exploiting weak security measures. Once hijacked, fraudsters can misuse the account for fraudulent activities or steal valuable virtual assets.
9. Social engineering: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that they wouldn’t normally do. In the Metaverse, fraudsters can employ social engineering techniques to trick users into sharing their login credentials, personal information, or even transferring virtual assets to them under false pretenses.
10. Data breaches: Metaverse platforms store vast amounts of user data, including personal information, payment details, and transaction history. Data breaches pose a significant risk, where unauthorized individuals gain access to this sensitive information. This can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, or the exposure of personal data, which can be exploited for various fraudulent purposes.
11. Money laundering: The Metaverse’s digital nature and potential anonymity can make it an attractive platform for money laundering. Fraudsters may use virtual currencies and complex transactions within the Metaverse to disguise the origins of illicit funds, making it challenging for authorities to track and prevent money laundering activities.
12. Lack of regulation and oversight: The Metaverse is a relatively new concept, and the legal and regulatory frameworks governing its operations are still evolving. The lack of comprehensive regulations and oversight can create an environment where fraudsters can exploit loopholes and carry out fraudulent activities with minimal consequences.
13. Inadequate user education and awareness: Users may be unaware of the various risks associated with the Metaverse and may not have the necessary knowledge or skills to protect themselves from fraud. Lack of awareness about phishing techniques, secure online practices, and common fraud schemes can make users more vulnerable to fraudulent activities.
To mitigate these risks, developers and platform operators in the Metaverse should prioritize security measures, such as robust user authentication mechanisms, encryption, secure storage of user data, regular audits of virtual economies, and education about online safety for users. Additionally, users should adopt best practices for online security, such as using strong and unique passwords, being cautious of suspicious links and requests for personal information, and keeping their software and devices up to date with the latest security patches.
Also read: Top 3 Metaverse Risks As Per Mark Zuckerberg
Top 10 Frauds that occur in Metaverse
The metaverse is a new and exciting world, but it’s also a place where fraudsters can thrive. Here are 10 of the most common metaverse frauds:
Phishing scams: In a phishing scam, fraudsters send fake emails or messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a metaverse platform or a cryptocurrency exchange. The emails or messages often contain links that, when clicked, take the victim to a fake website that looks like the real thing. Once the victim enters their personal information on the fake website, the fraudster can steal it.

Fake investment opportunities: Fraudsters often create fake investment opportunities in the metaverse. These investments may involve buying virtual land, NFTs, or other digital assets. The fraudsters promise high returns, but they often disappear with the victim’s money.
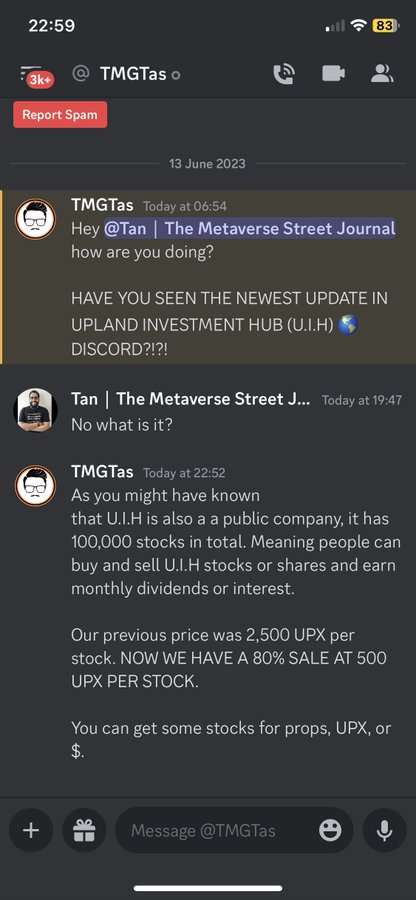
Scams involving NFTs: NFTs are digital assets that are stored on a blockchain. They can represent anything from artwork to virtual land. Fraudsters often create fake NFTs that look like real ones. They then sell these fake NFTs to unsuspecting victims.

Scams involving cryptocurrency: Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. It is often used in the metaverse to buy and sell goods and services. Fraudsters often create fake cryptocurrency exchanges or investment opportunities. They then steal the victim’s cryptocurrency.
Influencer fraud: In influencer fraud, fraudsters hack into the social media accounts of popular influencers. They then use these accounts to promote fake investment opportunities or NFTs. The fraudsters often target young people who are more likely to be influenced by their favorite influencers.
Data theft: Fraudsters can steal personal data from metaverse users in a variety of ways. They may hack into user accounts, steal data from virtual worlds, or trick users into giving up their personal information. Once they have the victim’s personal information, they can use it to commit identity theft, fraud, or other crimes.
Scams involving virtual goods: Virtual goods are items that can be purchased and used in virtual worlds. These goods can include clothing, accessories, weapons, and other items. Fraudsters often create fake virtual goods that look like real ones. They then sell these fake goods to unsuspecting victims.

Scams involving virtual worlds: Fraudsters often create fake virtual worlds that look like real ones. They then lure victims into these fake worlds and steal their personal information or money.
Scams involving metaverse events: Fraudsters often create fake metaverse events that look like real ones. They then lure victims to these fake events and steal their personal information or money.
Scams involving metaverse headsets: Fraudsters often create fake metaverse headsets that look like real ones. They then sell these fake headsets to unsuspecting victims. The fake headsets often contain malware that can steal the victim’s personal information or money.

These are just a few of the most common metaverse frauds. It’s important to be aware of these risks and to take steps to protect yourself.
How can you protect yourself from fraud in the Metaverse
Protecting yourself from fraud in the Metaverse requires a combination of proactive measures and cautious online behavior. Here are some key steps you can take to enhance your security and reduce the risk of fraud:
1. Choose reputable platforms: Stick to well-established and trusted Metaverse platforms. Research the platform’s reputation, security practices, and user reviews before creating an account or engaging in transactions. Popular platforms with robust security measures are more likely to have better protection against fraud.
2. Strong and unique passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for your Metaverse accounts. Avoid using easily guessable information such as your name or birthdate. Include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Using a password manager can help generate and securely store complex passwords.
3. Two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to provide a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your mobile device, in addition to your password. This can prevent unauthorized access even if your password is compromised.
4. Be cautious of phishing attempts: Be vigilant about phishing attempts, where fraudsters try to trick you into revealing your login credentials or personal information. Be wary of unsolicited emails, messages, or links asking for sensitive information. Verify the authenticity of communication before clicking on links or providing any information.
5. Use secure networks and devices: When accessing the Metaverse, use secure and trusted networks. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks, as they may be susceptible to eavesdropping or hacking. Keep your devices updated with the latest security patches and use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software.
6. Verify the legitimacy of virtual assets and transactions: Before purchasing or trading virtual assets, research the legitimacy of the items, sellers, or platforms involved. Be cautious of deals that seem too good to be true or require you to provide excessive personal or financial information. Use reputable marketplaces and verify the authenticity of the assets before making any transactions.
7. Regularly monitor your accounts: Keep a close eye on your Metaverse accounts and regularly review transaction history, virtual asset balances, and any suspicious activity. If you notice any unauthorized transactions or suspicious changes, report them to the platform’s support team immediately.
8. Educate yourself about fraud schemes: Stay informed about the latest fraud schemes in the Metaverse. Stay updated on common scams, phishing techniques, and emerging threats. This knowledge will help you recognize potential risks and take appropriate actions to protect yourself.
9. Protect your personal information: Be cautious about sharing personal information in the Metaverse. Avoid providing unnecessary details unless it’s required for legitimate purposes. Be particularly wary of platforms or individuals asking for sensitive information like your Social Security number, bank account details, or credit card information.
10. Report and seek support: If you encounter any fraudulent activity or believe you have been a victim of fraud in the Metaverse, report it to the relevant platform authorities or customer support. They can investigate the issue and take appropriate action. Additionally, seek assistance from local law enforcement or cybercrime reporting agencies to ensure the incident is properly documented.
11. Keep software and applications up to date: Regularly update your operating system, web browsers, and Metaverse applications to ensure you have the latest security patches and bug fixes. Outdated software can contain vulnerabilities that fraudsters can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your accounts or devices.
12. Use virtual wallets and secure payment methods: When making virtual purchases or transactions in the Metaverse, consider using secure payment methods like virtual wallets or reputable payment processors. These methods often provide an additional layer of security and can help protect your financial information.
13. Be cautious of third-party platforms and services: Exercise caution when using third-party platforms or services within the Metaverse. Be mindful of the permissions you grant and the information you share with these platforms. Stick to trusted and verified third-party providers to minimize the risk of fraudulent activities.
14. Research virtual marketplaces and sellers: Before engaging in virtual asset transactions, thoroughly research virtual marketplaces and sellers. Look for feedback, ratings, and reviews from other users to assess their credibility and reliability. Avoid dealing with unknown or unverified sellers, especially if they have a poor reputation.
15. Practice digital asset security: Safeguard your virtual assets by implementing proper security measures. Consider using secure digital wallets or storage solutions for your virtual currencies and assets. Use strong passwords, enable encryption when possible, and regularly back up your virtual asset data to prevent loss or theft.
16. Be wary of unsolicited investment opportunities: Exercise caution when approached with investment opportunities within the Metaverse that promise high returns. Be skeptical of schemes that seem too good to be true or require substantial upfront investments. Do thorough research, seek professional advice, and verify the legitimacy of the investment opportunity before committing any funds.
17. Maintain privacy settings: Review and adjust your privacy settings within Metaverse platforms to control the visibility of your personal information and activities. Limit the amount of personal information you share publicly and restrict access to your profile, virtual assets, and interactions to trusted individuals or groups.
18. Stay informed about platform policies and terms of service: Familiarize yourself with the policies, terms of service, and community guidelines of the Metaverse platforms you use. Understand the rules and regulations governing the platform, including their stance on fraud, disputes, and user responsibilities. Adhere to these guidelines to avoid unknowingly engaging in fraudulent activities.
19. Be cautious of unofficial or unofficially endorsed third-party tools: While third-party tools can enhance the Metaverse experience, exercise caution when using unofficial or unofficially endorsed tools. These tools may carry security risks or violate the terms of service of the Metaverse platforms. Stick to official tools or those recommended by trusted sources.
20. Trust your instincts and exercise skepticism: Trust your instincts and exercise skepticism when engaging in the Metaverse. If something feels suspicious or too good to be true, it’s wise to err on the side of caution. Question requests for personal information, be cautious of unsolicited approaches, and verify the legitimacy of offers or opportunities before taking any action.
Remember that maintaining awareness, adopting a skeptical mindset, and prioritizing security measures are essential in protecting yourself from fraud in the ever-evolving Metaverse landscape.
Jim Cramer has said. "These crypto assets all seem to be scams, and I want you out of them". #Bitcoin #Crypto #BTC #Binance #ETH #BNB #Twitter #News #NFT #Metaverse #PepeCoin #Pepe #Web3 #USDT #FTX #Lunc #Coinbase #Shiba #Doge #Floki #Dino #MemeCoin #Elon #Musk #SUI #XRP #USDT… pic.twitter.com/ksElk4wTek
— Fahad Faqeeh (@FahadFaqeeh65) June 7, 2023
By implementing these measures and maintaining a cautious approach, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to fraud in the Metaverse. Remember that staying informed, practicing good online hygiene, and using common sense are vital in safeguarding your virtual identity and assets.
Also read: Investing in the Metaverse: Risks and Rewards
Future of Metaverse
The future of the metaverse holds vast potential for transforming the way we live, work, and interact with digital environments. While the metaverse is still in its early stages, several trends and possibilities can shape its future. Here is a detailed exploration of what the future of the metaverse could look like:
1. Expanded Virtual Worlds: The metaverse is likely to expand with the creation of more virtual worlds and interconnected environments. These worlds may cater to various interests, such as gaming, entertainment, education, socializing, and professional collaboration. Each virtual world could offer unique experiences, rules, and ecosystems, allowing users to explore and engage with diverse virtual environments.
2. Seamless Cross-Platform Integration: The future metaverse is expected to offer seamless integration across platforms, devices, and technologies. Users will be able to access the metaverse from different devices, including virtual reality headsets, augmented reality glasses, smartphones, and computers. Cross-platform compatibility will enable users to transition seamlessly between virtual and physical environments, ensuring a consistent and immersive experience.
3. Realistic Virtual Reality: Advancements in virtual reality (VR) technology will contribute to more realistic and immersive virtual experiences within the metaverse. Enhanced graphics, haptic feedback, and sensory stimulation will make virtual environments feel increasingly lifelike. Users will be able to interact with virtual objects and other users in more natural and intuitive ways, blurring the line between the virtual and physical worlds.
4. Augmented Reality Integration: Augmented reality (AR) will play a significant role in the future of the metaverse. AR overlays digital content onto the real world, allowing users to interact with virtual objects and information within their physical environment. The metaverse could integrate AR technology, enabling users to access virtual content and experiences while still being aware of their surroundings. This could revolutionize areas such as navigation, education, retail, and entertainment.
5. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: The metaverse will likely integrate with the Internet of Things (IoT), creating a connected and intelligent environment. IoT devices embedded in the physical world can interact with the metaverse, enabling seamless data exchange and integration. Users will be able to control and monitor physical objects, such as home appliances, vehicles, and wearable devices, within the metaverse, enhancing convenience and personalization.
6. Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Assistants: Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a crucial role in the future metaverse. AI-powered virtual assistants will provide personalized and context-aware experiences, assisting users in navigating virtual environments, managing tasks, and accessing information. Virtual assistants will leverage natural language processing and machine learning capabilities, becoming more intelligent and responsive over time.
7. Virtual Economy and Cryptocurrencies: The metaverse is likely to see the rise of a robust virtual economy, where users can create, buy, sell, and trade virtual goods, services, and assets. Virtual currencies, such as cryptocurrencies or digital tokens, will facilitate transactions and enable the exchange of value within the metaverse. The virtual economy will encompass various industries, including gaming, virtual real estate, art, fashion, and entertainment.
8. Social and Community Interactions: The metaverse will foster social interactions and community building on a global scale. Users will be able to connect with people from around the world, participate in virtual events, and collaborate in virtual spaces. Social platforms within the metaverse will provide tools for communication, networking, and shared experiences, creating new opportunities for socializing, collaboration, and cultural exchange.
9. Personalized and Contextual Experiences: The future metaverse will prioritize personalized and context-aware experiences. Through data analytics, AI, and user preferences, virtual environments will adapt and tailor content, services, and recommendations to individual users. This will enhance user engagement, satisfaction, and the overall immersive experience within the metaverse
10. Governance and Regulations: As the metaverse expands, the need for governance and regulations will arise. Policies and guidelines will be necessary to ensure user safety, protect privacy, prevent abuse, address ethical concerns, and govern virtual economies. Stakeholders from various domains, including technology, government, and academia, will collaborate to establish standards and frameworks for metaverse governance.
11. Collaboration and Innovation: The metaverse will foster collaboration and innovation across industries. Companies, startups, and developers from diverse sectors will work together to create virtual experiences, services, and applications within the metaverse. Collaborative efforts will drive technological advancements, fuel creativity, and unlock new possibilities for business models and revenue streams.
12. Ethical Considerations and Digital Well-being: As the metaverse evolves, ethical considerations and digital well-being will become paramount. Ensuring user safety, privacy, and mental well-being will be critical. Designing responsible virtual experiences, addressing addiction risks, promoting digital balance, and mitigating the negative social impact will be essential to foster a healthy and inclusive metaverse ecosystem.
It’s important to note that the future of the metaverse is subject to various technological, social, and economic factors. The timeline and exact shape of the metaverse’s development will depend on advancements in technology, market demands, user adoption, and regulatory frameworks. As the metaverse continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly reshape how we interact with digital environments and create new opportunities for entertainment, education, collaboration, and commerce.


























































