A Comprehensive Guide To Unlocking The Power Of Blockchain Database

In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, blockchain has emerged as a revolutionary concept with the potential to transform various industries. At the core of this innovation is the blockchain database, a decentralized and secure system that has garnered significant attention. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the intricacies of blockchain databases, exploring their architecture, applications, and implications for the future.
Understanding Blockchain Database:
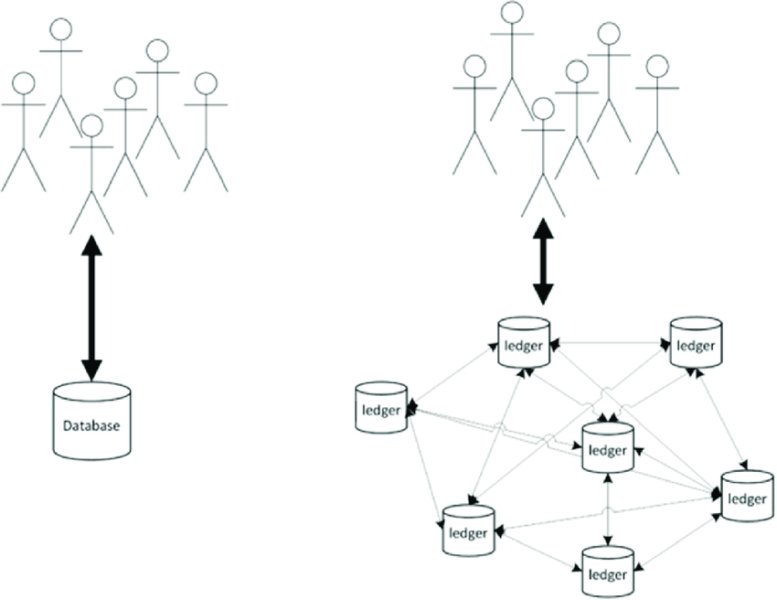
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that underlies cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. At its core, it’s a database that stores information across a network of computers, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key aspects of a blockchain database:
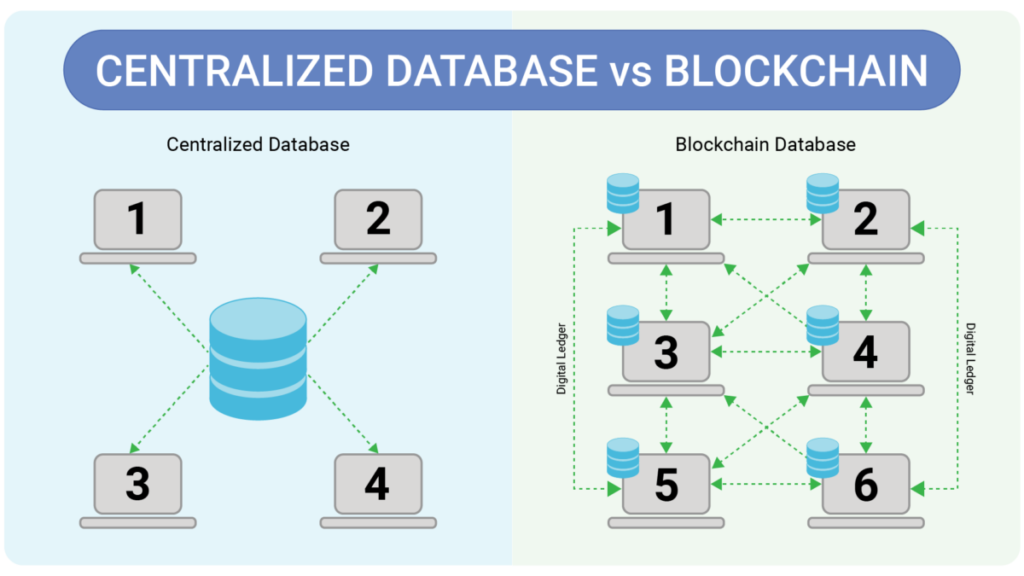
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases, blockchain doesn’t have a central authority. Information is stored on a network of computers (nodes) that work together to validate and record transactions. This decentralization eliminates the need for a single point of control, reducing the risk of manipulation or fraud.
- Blocks and Chains: Information is grouped into blocks, each containing a list of transactions. Once a block reaches a certain size or time limit, it’s added to the existing chain of blocks, forming a chronological sequence. This chain structure ensures a historical record of all transactions, making the entire process transparent and traceable.
- Consensus Mechanism: Nodes in a blockchain network must agree on the validity of transactions before adding them to the ledger. Various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (used in Bitcoin) or Proof of Stake, ensure that the majority of nodes reach a consensus. This process enhances the security of the database by preventing malicious actors from manipulating the system.
- Immutability: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it’s nearly impossible to alter or delete the information within it. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic techniques like hashing and ensures the integrity of the database. Any attempt to tamper with a block would require altering all subsequent blocks, a task that becomes increasingly difficult as more blocks are added.
- Smart Contracts: Many blockchain platforms support smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automate and enforce the execution of predefined rules, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing the efficiency of transactions.
- Cryptographic Security: Blockchain relies heavily on cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control access. Public and private keys are used to sign transactions, providing a secure and verifiable way of proving ownership.
Understanding the intricacies of a blockchain database is crucial for grasping its potential applications beyond cryptocurrencies, such as in supply chain management, voting systems, and healthcare. The decentralized and secure nature of blockchain technology continues to drive innovation across various industries.
Also, read – Blockchain Is The Next Era Of Database
The architecture of Blockchain Database:
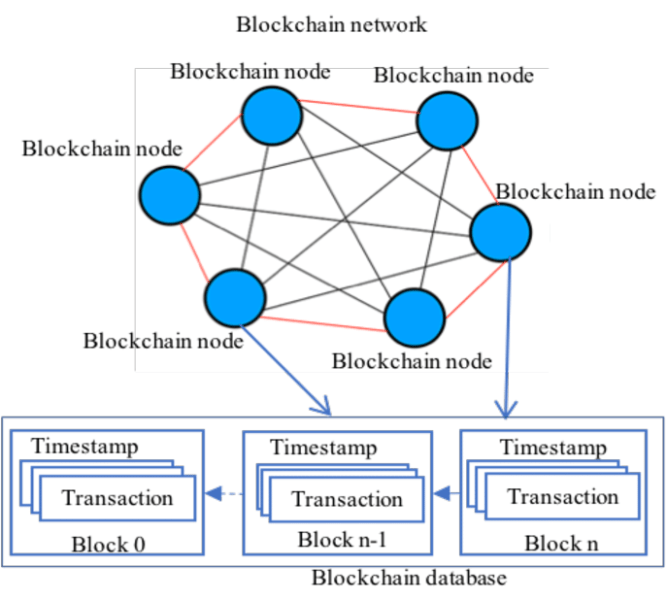
The architecture of a blockchain database is a crucial aspect that defines its structure and functionality. Let’s delve into the details of the key components that make up the architecture of a blockchain database:
- Nodes:
- At the foundation of the blockchain architecture are nodes, which are individual computers participating in the network. Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, providing redundancy and ensuring that the system remains decentralized.
- Blocks:
- Information in a blockchain is organized into blocks, each containing a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes, forming a chain. The size and frequency of block creation depend on the specific blockchain protocol.
- Consensus Mechanism:
- The consensus mechanism is a critical component that enables nodes to agree on the state of the blockchain. Different blockchains use various consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (used by Bitcoin) or Proof of Stake. These mechanisms ensure that nodes in the network reach an agreement before adding a new block to the chain.
- Cryptographic Hashing:
- Cryptographic hashes play a pivotal role in securing the integrity of the blockchain. Each block contains a hash of the previous block, creating a continuous chain. This makes it extremely difficult for anyone to alter a block without changing all subsequent blocks, providing a high level of security.
- Transactions:
- Transactions are the fundamental units of data stored in blocks. They include information about the sender, recipient, and the amount being transferred. Smart contracts, if supported by the blockchain, also form a part of transactions, containing programmable logic to automate certain actions when predefined conditions are met.
- Merkle Trees:
- To efficiently verify the contents of a block, a Merkle tree structure is often employed. This hierarchical arrangement of hashes allows for quick confirmation of the integrity of transactions within a block.
- Smart Contracts:
- Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They reside on the blockchain and automatically execute predefined actions when specific conditions are met. This feature enhances the capabilities of blockchain beyond simple value transfers.
- Wallets and Keys:
- Users interact with the blockchain through wallets, which store their public and private keys. Public keys serve as addresses for receiving funds, while private keys are used to sign transactions, providing a secure and verifiable means of ownership.
- Network Protocol:
- The communication between nodes is facilitated by a network protocol. This protocol defines how nodes share information, propagate transactions, and reach consensus. Examples include Bitcoin’s peer-to-peer protocol or Ethereum’s Ethereum Wire Protocol (EWP).
Understanding the architecture of a blockchain database is essential for developers, blockchain enthusiasts, and businesses looking to leverage this technology. It provides insights into how data is structured, secured, and maintained in a decentralized and transparent manner.
This has been my vision for the past 2 years & I'm glad more people like the CEO of Roblox are thinking along the same lines.
NFTs moving across platforms.
This is how you capitalize on blockchain technology, an immutable public database everyone has access to the information… pic.twitter.com/NpE7yztgmj
— Elvis (@ElvisMounzer) November 13, 2023
Applications of Blockchain Databases:
Blockchain databases have transcended their origins in cryptocurrencies and are finding applications across various industries. Here’s an in-depth exploration of the diverse applications of blockchain databases:
- Cryptocurrencies:
- The first and most well-known application of blockchain is in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to conduct peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
- Smart Contracts:
- Blockchain enables the creation and execution of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts have programmable logic written into the code, automating and enforcing the terms of an agreement. They find applications in various fields, including legal processes, supply chain management, and insurance.
- Supply Chain Management:
- Blockchain enhances transparency and traceability in supply chains. Each step in the supply chain, from production to distribution, can be recorded on the blockchain. This reduces the risk of fraud, ensures product authenticity, and improves overall efficiency.
- Healthcare:
- In healthcare, blockchain can be used to secure and streamline the sharing of patient data among different healthcare providers. Patients have more control over their data, and the decentralized nature of blockchain ensures data integrity and security.
- Identity Management:
- Blockchain provides a secure and decentralized solution for identity management. Users can control access to their personal information, reducing the risk of identity theft. Governments and organizations are exploring blockchain for creating digital identities.
- Voting Systems:
- Blockchain can be applied to create secure and transparent voting systems. Each vote is recorded on the blockchain, providing an immutable and auditable trail. This can significantly reduce the risk of fraud and enhance the integrity of electoral processes.
- Financial Services:
- Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is transforming traditional financial services. It facilitates faster and more cost-effective cross-border transactions, improves transparency in financial processes, and enables the creation of new financial instruments.
- Real Estate:
- Blockchain is used in real estate to streamline property transactions. Smart contracts can automate the transfer of ownership, and blockchain ensures the transparency of property records, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Intellectual Property Protection:
- Blockchain can be employed to establish and protect intellectual property rights. It provides a tamper-proof and time-stamped record of creations, making it easier to prove ownership and track the use of intellectual property.
- Energy Trading:
- In the energy sector, blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading. Producers of renewable energy can sell excess energy directly to consumers, and blockchain ensures transparent and automated transactions.
- Food Safety:
- Blockchain can be used to track the origin and journey of food products from farm to table. This transparency helps in quickly identifying and addressing issues related to food safety.
- Gaming and Digital Assets:
- Blockchain is employed in gaming for secure and transparent transactions of in-game assets. Players have true ownership of their digital assets, and blockchain ensures the scarcity and authenticity of virtual items.
Understanding the diverse applications of blockchain databases is crucial for businesses and innovators seeking to leverage this technology to enhance efficiency, security, and transparency across various sectors.
What is a Blockchain?
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. Here are some key points about blockchain:
Definition: A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among… pic.twitter.com/7pnaK82jtC
— Stephen Duke (@stephe11349) October 18, 2023
Implications for the Future:
1. Reshaping Governance:
- Blockchain’s decentralized nature has the potential to transform governance structures. Transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping can enhance accountability in public administration. Smart contracts could automate certain government functions, reducing bureaucracy and improving efficiency.
2. Enhancing Cybersecurity:
- Blockchain’s cryptographic techniques make it highly secure, offering protection against data tampering and unauthorized access. As cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, the adoption of blockchain in various industries could provide a robust defense mechanism, safeguarding sensitive information.
3. New Economic Models:
- Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, enabling the creation of decentralized economic systems. Cryptocurrencies and token economies are just the beginning; blockchain has the potential to redefine how value is exchanged and distributed, challenging traditional economic models.
4. Financial Inclusion:
- The decentralized and borderless nature of blockchain opens up new opportunities for financial inclusion. Individuals without access to traditional banking systems can participate in the global economy through blockchain-based financial services, such as digital wallets and microtransactions.
5. Cross-Border Transactions:
- Blockchain streamlines cross-border transactions by providing a faster and more cost-effective alternative to traditional banking systems. This can have significant implications for international trade and finance, reducing transaction costs and improving the efficiency of global supply chains.
Challenges and Considerations:

1. Scalability:
- One of the primary challenges facing blockchain is scalability. As the number of transactions increases, some blockchain networks experience congestion and slower transaction times. Scalability solutions, such as layer 2 protocols and advancements in consensus algorithms, are actively being developed to address this limitation.
2. Energy Consumption:
- The energy consumption associated with certain consensus mechanisms, particularly Proof of Work, has raised environmental concerns. The future of blockchain must consider more energy-efficient consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Stake, to mitigate the environmental impact and promote sustainability.
3. Regulatory Hurdles:
- The regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Striking a balance between fostering innovation and addressing concerns related to fraud, money laundering, and consumer protection is essential. Clear and well-defined regulations will play a crucial role in the widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
4. Interoperability:
- Interoperability between different blockchain networks and with traditional systems is a key consideration for the future. Efforts are underway to create standards and protocols that enable seamless communication between diverse blockchain platforms, promoting a more connected and interoperable ecosystem.
5. Privacy Concerns:
- While blockchain provides transparency, there are challenges related to privacy. Striking the right balance between transparency and protecting sensitive information is critical. Advancements in privacy-focused technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs, aim to address these concerns.
6. Educational Barriers:
- The complexity of blockchain technology poses a challenge for widespread adoption. Overcoming educational barriers and increasing awareness among businesses, policymakers, and the general public is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain.
The future implications of blockchain are vast and transformative. Overcoming challenges and addressing considerations will require collaborative efforts from the global community, including technological innovations, regulatory frameworks, and educational initiatives. As blockchain continues to mature, its impact on the way we govern, transact, and interact with technology is likely to be revolutionary.
Conclusion:
Blockchain databases represent a paradigm shift in the way we store and manage data. As technology advances and the world becomes increasingly digitized, understanding the intricacies of blockchain databases is essential. This comprehensive guide serves as a roadmap to navigate the fascinating world of blockchain databases, unlocking their potential for a decentralized and secure future.




























































