The Development Of Blockchain In The Last 5 Years: Top 10 New Things In The Blockchain World

Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has gained significant attention and transformed various industries since its inception. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable ledger that securely records transactions or data across multiple computers or nodes. It provides a transparent and tamper-proof system for storing and verifying information without the need for intermediaries.
The fundamental concept of blockchain revolves around creating a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of data, timestamp, and a unique identifier called a hash. The data within a block can vary depending on the specific blockchain application, but it commonly includes transaction details, such as sender, recipient, and amount.
The hash, a digital fingerprint of the block, is generated using a cryptographic algorithm. It ensures the integrity of the data within the block and any changes made to the block will result in a different hash. Additionally, each block also contains the hash of the previous block, forming a chronological chain that links all the blocks together.
One of the key features of blockchain is decentralization. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single entity or authority controls the data, blockchain distributes the ledger across multiple nodes or computers within a network. These nodes work together to validate and store transactions, maintaining a consensus on the state of the blockchain. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries and provides transparency, as all participants can view the entire transaction history.
To add new transactions to the blockchain, a consensus mechanism is employed. Different blockchain networks use various consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and more. These algorithms ensure that all participants agree on the validity and order of transactions, preventing double-spending and fraud.
Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or remove. As subsequent blocks contain the hash of the previous block, any modification to a block would require changing all subsequent blocks, which is computationally expensive and practically infeasible. This immutability and tamper-proof nature make blockchain highly secure and reliable for storing sensitive information.
Blockchain technology has found its most notable application in cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin being the first and most well-known example. However, the potential uses of blockchain extend far beyond digital currencies. It has been applied in supply chain management, healthcare, finance, voting systems, intellectual property protection, and more.
In supply chain management, blockchain enables traceability and transparency by recording each transaction and movement of goods. This helps prevent counterfeit products, ensures fair labor practices, and enhances efficiency by reducing paperwork and eliminating intermediaries.
In the healthcare industry, blockchain can securely store and share patient data, ensuring privacy and interoperability. It allows patients to have control over their medical records and enables healthcare providers to access accurate and up-to-date information.
In the financial sector, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize processes such as cross-border payments, remittances, and smart contracts. It can significantly reduce costs, increase transaction speed, and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
Overall, blockchain technology offers a secure, transparent, and decentralized solution for various industries, providing trust and efficiency in an increasingly digitized world. Its potential impact is vast, and as the technology continues to evolve, it is likely to revolutionize numerous sectors and reshape the way we interact, transact, and store data.
Importance of Blockchain for the economy
Blockchain technology holds immense importance for the economy, offering several potential benefits and transformative opportunities. Here are some key aspects highlighting the significance of blockchain in the economic landscape:
1. Enhanced Efficiency: Blockchain has the potential to streamline numerous processes and eliminate inefficiencies in various sectors. By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, it reduces the need for intermediaries, paperwork, and manual reconciliation. This leads to faster transaction settlements, reduced costs, and increased operational efficiency, benefiting businesses and consumers alike.
2. Transparent and Trustworthy Transactions: Trust is a crucial element in economic transactions. Blockchain’s transparency and immutability enable participants to have a clear view of the transaction history and verify the authenticity of data without relying on a centralized authority. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud, corruption, and manipulation, fostering trust between parties and enhancing overall economic integrity.
3. Secure Data Management: Data security is a critical concern in the digital era. Blockchain’s cryptographic algorithms and decentralized architecture make it highly resistant to hacking and tampering. By distributing data across multiple nodes and ensuring consensus, blockchain provides a secure and reliable environment for storing sensitive information. This can have significant implications for sectors handling financial data, personal information, and intellectual property.
4. Financial Inclusion and Access: Blockchain has the potential to improve financial inclusion by providing services to the unbanked and underbanked populations. Through decentralized cryptocurrencies and digital wallets, individuals in underserved regions can access financial services, make transactions, and participate in the global economy. Blockchain’s low transaction fees and borderless nature also facilitate cross-border remittances and improve financial accessibility for migrant workers.
5. Supply Chain Optimization: The global supply chain is complex, involving numerous intermediaries and stages. Blockchain technology can revolutionize supply chain management by enhancing transparency, traceability, and efficiency. By recording every transaction and movement of goods, stakeholders can track the origin, manufacturing processes, and distribution of products in real-time. This helps combat counterfeit products, ensure fair trade practices, reduce fraud, and enhance consumer trust.
6. Smart Contracts and Automation: Blockchain’s programmable feature enables the development of smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with predefined conditions. Smart contracts can automate complex processes, such as financial transactions, insurance claims, and royalty distributions. By removing the need for intermediaries and reducing manual intervention, smart contracts enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and mitigate disputes, leading to significant economic benefits.
7. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Blockchain technology fosters innovation and empowers entrepreneurs to develop decentralized applications (DApps) and new business models. The blockchain ecosystem encourages collaboration, as developers can build on existing platforms and leverage decentralized networks. This can spur economic growth, job creation, and the emergence of disruptive solutions across industries.
8. Data Monetization and Privacy: Blockchain allows individuals to have control over their personal data and monetize it selectively. Users can choose to share their data securely and receive compensation directly from interested parties. This data ownership and privacy model empower individuals and provide economic incentives for data sharing, leading to more accurate market insights and personalized services.
In summary, blockchain technology’s importance for the economy lies in its potential to enhance efficiency, transparency, security, and trust in economic transactions. By revolutionizing various sectors and enabling new business models, blockchain has the capacity to drive economic growth, foster innovation, improve financial inclusion, and reshape the way we interact and transact in the digital world.
Also read: Top 10 Tips To Start A Blockchain Startup: Is Blockchain The Future
Top 10 New things in the Blockchain World
Blockchain technology is constantly evolving, and there are always new and exciting developments happening. Here are 10 of the most promising new things in the blockchain world in 2023:
- The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi is a financial system that is built on blockchain technology and does not rely on traditional financial institutions. DeFi applications are growing in popularity, and they offer a number of benefits, such as lower fees, greater transparency, and more security.

- The growth of non-fungible tokens (NFTs). NFTs are unique digital assets that cannot be replaced. They have been used to represent a variety of things, such as artworks, collectibles, and even real estate. The NFT market is growing rapidly, and it is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.

- The development of more scalable blockchain platforms. One of the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As the number of users and transactions on blockchain networks increases, the networks can become slow and congested. There are a number of new blockchain platforms that are being developed to address this challenge.

- The increasing adoption of blockchain by businesses. Businesses are starting to realize the potential benefits of blockchain technology. They are using blockchain to improve their supply chains, track their assets, and manage their payments. The adoption of blockchain by businesses is expected to grow in the years to come.
- The development of new blockchain-based applications. Blockchain technology is being used to develop a wide range of new applications. These applications include healthcare records management, voting systems, and supply chain management. The development of new blockchain-based applications is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.

- The increasing regulation of blockchain technology. As blockchain technology becomes more widely adopted, governments are starting to regulate it. This regulation is aimed at protecting consumers and businesses. The regulation of blockchain technology is expected to continue to evolve in the years to come.
- The growth of the blockchain community. The blockchain community is growing rapidly. There are now a number of conferences, meetups, and online forums where people can learn about and discuss blockchain technology. The growth of the blockchain community is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
- The increasing awareness of blockchain technology. The general public is becoming more aware of blockchain technology. This is due to the increasing media coverage of blockchain and the growing number of businesses that are adopting the technology. The increasing awareness of blockchain technology is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
- The development of new blockchain education programs. There is a growing demand for blockchain education. There are now a number of universities and colleges that offer blockchain courses. The development of new blockchain education programs is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
- The launch of new blockchain startups. There is a growing number of blockchain startups being launched. These startups are developing new blockchain-based applications and services. The launch of new blockchain startups is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
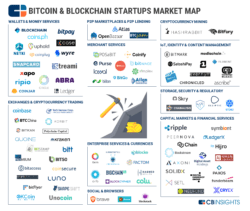
These are just 10 of the most promising new things in the blockchain world in 2023. Blockchain technology is constantly evolving, and there are sure to be even more exciting developments in the years to come.
Learning Blockchain Development?
GPT4 is the hack of all hacks.
If you know how to use it correctly, you’ll cut your learning curve in half.
If you don’t – you’ll learn nothing.
Phrase your prompts for guidance.
It should never be a done-for-you service provider.
— James Kane (@_jtkane) June 22, 2023
Development of Blockchain in last 5 years
Over the past five years, blockchain technology has undergone significant development and witnessed notable advancements across various fronts. Here is an overview of the key developments in the blockchain space during this period:
1. Mainstream Adoption of Cryptocurrencies: The last five years have witnessed a surge in the adoption and acceptance of cryptocurrencies, led by Bitcoin and followed by other prominent digital currencies such as Ethereum, Ripple, and Litecoin. This increased acceptance has paved the way for the wider adoption of blockchain technology as a whole.
2. Expansion of Blockchain Applications: Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has found applications in numerous industries. From supply chain management and healthcare to finance and governance, organizations and governments worldwide have explored blockchain’s potential to improve efficiency, transparency, and security in various sectors.
3. Emergence of Enterprise Blockchain Solutions: Enterprises have started embracing blockchain technology to enhance their operations. Several major players, including IBM, Microsoft, and Oracle, have developed enterprise-grade blockchain platforms that offer enhanced scalability, privacy, and security features tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses.
4. Interoperability and Scalability Solutions: Interoperability and scalability have been critical challenges for blockchain networks. In response, various projects have emerged to address these issues. Initiatives such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and interoperability protocols like Interledger aim to create seamless connections between different blockchains, enabling data and value transfer across networks. Additionally, Layer 2 solutions like Lightning Network and sidechains have emerged to improve scalability and transaction throughput.
5. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): DeFi has emerged as a prominent sector within the blockchain ecosystem. DeFi protocols leverage smart contracts to provide decentralized lending, borrowing, yield farming, and other financial services. This has enabled users to access traditional financial services without intermediaries. Additionally, the rise of NFTs has revolutionized digital ownership and provenance, enabling the creation and trading of unique digital assets, including art, collectibles, and virtual real estate.
6. Regulatory Developments: Governments and regulatory bodies have been actively working to establish frameworks and guidelines for blockchain and cryptocurrencies. While regulations differ across jurisdictions, efforts to provide clarity and address concerns related to security, privacy, money laundering, and consumer protection have been observed. Regulatory developments aim to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring compliance.
7. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Blockchain’s energy consumption has been a topic of discussion. In recent years, various projects have focused on improving the energy efficiency of blockchain networks. New consensus algorithms like Proof of Stake (PoS) have gained traction as they require significantly less energy compared to Proof of Work (PoW) algorithms, which are used by Bitcoin. Furthermore, initiatives are being undertaken to explore the use of renewable energy sources for blockchain mining operations.
8. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT): The integration of blockchain with emerging technologies like AI and IoT has gained attention. Combining blockchain with AI allows for secure data sharing, privacy preservation, and the development of autonomous decentralized applications. Blockchain also enables the secure and decentralized management of IoT devices, facilitating improved data integrity, trust, and interoperability in IoT ecosystems.
9. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Central banks around the world have been exploring the concept of CBDCs, which are digital representations of fiat currencies issued and regulated by central authorities. These digital currencies leverage blockchain or distributed ledger technology to provide enhanced security, efficiency, and financial inclusion. Several countries, including China, Sweden, and the Bahamas, have made significant progress in piloting and implementing CBDCs.
Overall, the past five years have seen substantial advancements in the development and adoption of blockchain technology. From cryptocurrencies and enterprise solutions to DeFi, NFTs, and regulatory frameworks, blockchain has evolved and matured as a transformative technology. As it continues to progress, blockchain holds the potential to reshape various industries, enhance trust and transparency, and drive economic growth in the years to come.
Also read: The Top 10 Blockchain Projects To Watch In 2023
Risks associated with Blockchain Development
While blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, it is important to acknowledge and understand the potential risks and challenges associated with its development and implementation. Here are some key risks related to blockchain:
1. Security Vulnerabilities: Despite blockchain’s reputation for security, there are potential vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Smart contract bugs, coding errors, and vulnerabilities in blockchain platforms can lead to hacking, theft of digital assets, or unauthorized access. Additionally, if a single entity gains control of the majority of a blockchain’s computing power (known as a 51% attack), they could manipulate transactions and undermine the integrity of the network.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Blockchain technology operates in a regulatory grey area in many jurisdictions. Uncertainty surrounding compliance and regulatory frameworks can create challenges for businesses and individuals utilizing blockchain. The lack of clear guidelines and varying interpretations of existing regulations may lead to legal and compliance risks, hindering widespread adoption and development.
3. Scalability and Performance Challenges: Blockchain networks face scalability limitations due to the consensus mechanisms they employ. For example, public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have experienced congestion and slow transaction processing times during periods of high demand. Achieving scalability while maintaining decentralization and security remains a significant technical challenge that requires further innovation.
4. Governance and Coordination Issues: Blockchain networks typically involve multiple participants with potentially conflicting interests. Establishing effective governance models and decision-making processes can be challenging, particularly when multiple stakeholders are involved. Resolving disputes, implementing protocol upgrades, and ensuring consensus among network participants can be complex and time-consuming.
5. Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact: Some blockchain networks, particularly those utilizing Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, consume substantial amounts of energy. This high energy consumption contributes to environmental concerns, especially as the demand for blockchain technology grows. However, it’s worth noting that newer consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) aim to address these environmental issues by reducing energy consumption.
6. Privacy and Data Protection: While blockchain offers transparency, the inherent nature of the technology makes it challenging to ensure privacy and data protection. On public blockchains, transaction details are visible to all participants, which may conflict with the privacy requirements of certain applications. Efforts are being made to develop privacy-enhancing technologies and techniques like zero-knowledge proofs to address this challenge.
7. Interoperability and Standardization: The lack of interoperability and standardization among different blockchain networks and platforms hinders seamless data and value transfer. This fragmentation limits the potential benefits of blockchain technology and creates complexities when integrating blockchain with existing systems or between different blockchain networks.
8. User Experience and Adoption Hurdles: Blockchain applications often require users to manage private keys and navigate unfamiliar user interfaces, which can be a barrier to adoption. Improving the user experience and creating intuitive interfaces that hide the complexities of blockchain technology is crucial for mainstream adoption.
9. Economic and Financial Risks: Volatility and market fluctuations in cryptocurrencies, which often operate on blockchain networks, pose economic risks. Users may face financial losses due to price volatility, scams, fraudulent initial coin offerings (ICOs), or Ponzi schemes associated with certain blockchain projects.
Addressing these risks requires a comprehensive approach involving robust security measures, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and industry collaboration. As blockchain technology evolves, efforts to mitigate risks and find solutions to these challenges will be instrumental in harnessing the full potential of this transformative technology.
Also read: 15 Blockchain Risks Every CIO Should Know About
Future of Blockchain Development
The future of blockchain development holds immense potential for further innovation and widespread adoption across various industries. Here are some key trends and possibilities that may shape the future of blockchain:
1. Scalability Solutions: Enhancing scalability is a crucial focus for blockchain developers. Various solutions, such as sharding, layer 2 protocols, and improved consensus algorithms, are being explored to increase transaction throughput and accommodate the growing demands of blockchain networks. Advancements in scalability will enable broader adoption and support the integration of blockchain technology into large-scale applications.
2. Interoperability and Cross-Chain Communication: The interoperability challenge is being addressed through the development of interoperability protocols and frameworks. These solutions aim to facilitate seamless communication and data transfer between different blockchain networks. Interoperability will enable the exchange of assets, data, and services across disparate blockchains, unlocking new possibilities for decentralized applications and ecosystems.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies: Blockchain’s convergence with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing will lead to transformative applications. Combining blockchain with AI can enable secure and decentralized machine learning models, while integrating blockchain with IoT can enhance data integrity, trust, and interoperability in connected device networks. Such synergies will open up new avenues for innovation and value creation.
4. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Advancements in privacy-enhancing technologies within the blockchain space are gaining traction. Techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation, and homomorphic encryption allow for privacy-preserving transactions and data sharing while still maintaining the transparency and integrity of blockchain networks. These developments will address concerns around data privacy and enable the adoption of blockchain in industries with stringent privacy requirements.
5. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): The exploration and implementation of CBDCs by central banks are expected to continue in the coming years. CBDCs leverage blockchain or distributed ledger technology to digitize fiat currencies, offering benefits such as faster transactions, enhanced transparency, and financial inclusion. As more countries pilot and adopt CBDCs, blockchain technology will play a pivotal role in reshaping the global financial landscape.
6. Governance and Standards Development: The establishment of governance models, industry standards, and regulatory frameworks will be critical for the maturation and mainstream adoption of blockchain technology. Regulatory clarity will provide certainty for businesses, while governance models will enable effective decision-making and coordination within blockchain networks. Standardization efforts will enhance interoperability, security, and compatibility among different blockchain implementations.
7. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: Blockchain’s energy consumption has raised concerns about its environmental impact. Efforts are being made to improve energy efficiency and explore greener alternatives, such as transitioning from energy-intensive consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) to more energy-efficient mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS). The future of blockchain development will prioritize sustainability and seek environmentally friendly solutions.
8. Industry-Specific Applications: Blockchain’s potential spans across various industries, and its adoption will continue to accelerate in sectors such as supply chain management, healthcare, finance, energy, and governance. Customized blockchain solutions tailored to meet industry-specific requirements will drive efficiency, transparency, and trust within these sectors, leading to significant advancements and disruptive innovations.
9. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Evolution: DeFi has emerged as a significant trend within the blockchain space, revolutionizing traditional financial services. The future of blockchain development will witness further advancements in DeFi protocols, decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and liquidity mechanisms. DeFi will continue to expand its offerings, providing more sophisticated financial instruments and services to users worldwide.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, collaboration among developers, researchers, businesses, and regulators will be crucial in shaping its future. With ongoing advancements and the exploration of new use cases, blockchain is poised to revolutionize numerous aspects of our digital infrastructure and transform industries on a global scale.




























































