Top 10 Ethereum Blockchain Innovations Driving Adoption And Growth

Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that enables the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). It was proposed by Vitalik Buterin in late 2013 and officially launched on July 30, 2015. Ethereum’s native cryptocurrency is called Ether (ETH), which is used to facilitate transactions and incentivize participants on the network.
At its core, Ethereum is a decentralized platform that allows developers to build and deploy smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions written into code. They automatically execute transactions and actions when specific conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries or third parties.
Ethereum introduced the concept of a Turing-complete programming language within its blockchain, allowing developers to create complex and highly customizable decentralized applications. This flexibility has led to the rapid growth of the Ethereum ecosystem and the development of various decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized exchanges, and much more.
Ethereum operates on a distributed network of computers called nodes. These nodes maintain a copy of the entire Ethereum blockchain and work together to validate and record transactions. This decentralized nature ensures that there is no central point of control or failure, making the network resilient to censorship and single points of failure.
The Ethereum blockchain uses a consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-Work (PoW), although there are plans to transition to a more energy-efficient consensus algorithm called Proof-of-Stake (PoS) with the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. PoW requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network. Miners are rewarded with Ether for their computational efforts.
Ethereum’s blockchain consists of a series of blocks, each containing a list of transactions and a reference to the previous block, creating a chronological chain of data. This ensures the immutability and integrity of the blockchain. Ethereum also allows for the storage of data and the execution of code within its blockchain, enabling developers to create decentralized applications that are censorship-resistant and tamper-proof.
The Ethereum ecosystem is supported by a vibrant community of developers, entrepreneurs, and enthusiasts. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a runtime environment that executes smart contracts on the Ethereum network. It enables developers to write code in various programming languages, including Solidity (Ethereum’s native language), Vyper, and others.
In addition to its role as a platform for creating DApps, Ethereum has its own economy and serves as a financial instrument. Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency, can be used for various purposes within the Ethereum ecosystem. It can be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges, used to pay for transaction fees (gas) when executing smart contracts or transferring tokens, and staked to participate in the network’s consensus mechanism.
Overall, Ethereum has revolutionized the blockchain industry by providing a powerful platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts. Its open nature, flexibility, and growing ecosystem have made it a popular choice for developers and entrepreneurs seeking to build innovative and transparent applications in a decentralized manner.
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that allows multiple participants to maintain a shared, tamper-resistant, and transparent record of transactions or information. It was originally introduced as the underlying technology for the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but its potential applications have expanded far beyond digital currencies.
At its core, a blockchain is a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions or data. These blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes, creating a chronological and immutable record of all transactions or information stored on the blockchain.
The key features of blockchain technology are decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability.
Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems where a central authority, such as a bank or government, maintains and controls the data, a blockchain operates in a decentralized manner. It is distributed across multiple computers or nodes that participate in the network. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain, and transactions are validated and added to the ledger through a consensus mechanism agreed upon by the network participants. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries and creates a trustless environment where participants can interact directly with one another.
Transparency: Blockchain provides transparency by allowing anyone to view the transactions or information recorded on the blockchain. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes visible to all participants in the network. This transparency promotes accountability and reduces the potential for fraud or manipulation since the data is open and verifiable by anyone.
Security: Blockchain ensures the security of transactions and data through cryptographic techniques. Each transaction or block is secured using a cryptographic hash, which is a unique digital fingerprint generated by an algorithm. Any modification to the data within a block would result in a different hash, making it easily detectable. Moreover, blockchain’s decentralized nature and consensus mechanism make it highly resistant to attacks or unauthorized changes. To alter a transaction or block, an attacker would need to control the majority of the network’s computing power, making it computationally infeasible and economically unviable.
Immutability: Once a transaction or block is added to the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to alter or delete it. This immutability is a result of the cryptographic linking between blocks and the decentralized consensus mechanism. As new blocks are added to the blockchain, they are linked to previous blocks using cryptographic hashes. This chaining of blocks makes it computationally expensive to alter past transactions, as it would require modifying all subsequent blocks as well. The immutability of blockchain provides a high level of data integrity and builds trust among participants.
Blockchain technology has expanded beyond cryptocurrencies and is now being explored and implemented in various industries and sectors. It has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management, voting systems, financial services, healthcare, identity verification, real estate, and more. Smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with predefined conditions written into code, can be deployed on blockchains to automate and enforce contractual obligations without the need for intermediaries.
However, it is important to note that blockchain technology also has its limitations. It can be computationally expensive and slower compared to centralized systems, and scaling the technology to handle large volumes of transactions is an ongoing challenge. Nevertheless, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving scalability and addressing other limitations to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology.
Also read: 10 Best Books To Learn About Ethereum To Understand Open- Source Blockchain
Relation between Ethereum and Blockchain
Ethereum is one of the most prominent implementations of blockchain technology. It is a decentralized blockchain platform that utilizes blockchain’s fundamental principles to enable the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps).
In essence, Ethereum is built upon the underlying blockchain infrastructure. It leverages the decentralized, transparent, secure, and immutable nature of blockchain to provide a platform for developers to build and deploy DApps and smart contracts. Ethereum extends the capabilities of blockchain beyond simple financial transactions by incorporating a Turing-complete programming language within its blockchain.
Here are the key aspects of the relation between Ethereum and blockchain:
1. Blockchain as the underlying technology: Ethereum is based on the concept of blockchain, which serves as the underlying technology that enables the secure and transparent recording of transactions. The Ethereum blockchain consists of a series of blocks, each containing a list of transactions and a reference to the previous block, creating a chronological chain of data. This blockchain architecture ensures the integrity and immutability of the recorded transactions.
2. Smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain: Ethereum introduced the concept of smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with predefined conditions written into code. These smart contracts are stored and executed on the Ethereum blockchain, taking advantage of the decentralized and transparent nature of blockchain. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), a runtime environment on the Ethereum network, executes the smart contracts. The blockchain serves as the secure and immutable platform to record and validate the execution of these contracts.
3. Decentralized applications (DApps): Ethereum allows developers to build decentralized applications (DApps) on its blockchain. DApps are software applications that run on a decentralized network of computers, rather than a single server or a centralized infrastructure. Ethereum provides developers with the tools, frameworks, and libraries to create and deploy DApps. These applications can interact with the Ethereum blockchain, execute smart contracts, and utilize the decentralized nature of the network.
4. Ethereum’s consensus mechanism: Ethereum initially used a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, similar to that of Bitcoin, to secure its blockchain and validate transactions. However, with the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, it is transitioning to a more energy-efficient consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Stake (PoS). The consensus mechanism determines how nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
5. Native cryptocurrency: Ethereum has its native cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH). Ether serves multiple purposes within the Ethereum ecosystem. It can be used to facilitate transactions, pay for gas fees (transaction fees) when executing smart contracts, and participate in the consensus mechanism by staking. The transfer of Ether and other tokens on the Ethereum blockchain is recorded and secured by the underlying blockchain technology.
In summary, Ethereum is a specific implementation of blockchain technology that extends its capabilities by allowing the execution of smart contracts and the development of decentralized applications. Ethereum utilizes blockchain’s decentralized, transparent, secure, and immutable properties to provide a platform for developers to create innovative applications and execute programmable contracts on a distributed network.
Importance of Ethereum and Blockchain for Economy
Ethereum and blockchain technology have significant implications for the economy, offering several important benefits and opportunities. Here are some of the key ways in which Ethereum and blockchain impact the economy:
1. Decentralization and disintermediation: Ethereum and blockchain technology enable decentralized systems, removing the need for intermediaries such as banks, financial institutions, or centralized authorities. This disintermediation reduces costs, streamlines processes, and increases efficiency in various economic activities, including financial transactions, supply chain management, and identity verification. By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain technology can potentially democratize access to financial services, promote financial inclusion, and reduce economic inequality.
2. Trust and transparency: Blockchain’s transparent and immutable nature enhances trust and accountability in economic transactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that all participants have access to the same information, eliminating information asymmetry and reducing the potential for fraud and manipulation. This transparency can enhance the integrity of financial transactions, improve auditing processes, and enable stakeholders to make more informed decisions based on verified and auditable data.
3. Smart contracts and automation: Ethereum’s smart contract functionality allows for the automation of agreements and contractual obligations. Smart contracts are self-executing and self-enforcing, eliminating the need for intermediaries to facilitate and enforce contracts. This automation streamlines business processes, reduces administrative costs, and increases efficiency in sectors such as insurance, real estate, supply chain management, and more. Smart contracts can also reduce the risk of contract disputes, as the terms and conditions are predefined in code and automatically executed based on predetermined conditions.
4. Innovation and new business models: Ethereum and blockchain technology have unleashed a wave of innovation and the creation of new business models. The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for the development of decentralized applications (DApps) and the tokenization of assets. This opens up new opportunities for crowdfunding, peer-to-peer lending, decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and more. These innovations have the potential to reshape traditional industries, unlock liquidity, and provide alternative investment avenues for individuals and businesses.
5. Financial inclusion and access: Ethereum and blockchain can enhance financial inclusion by providing access to financial services to the unbanked and underbanked populations. Through the use of blockchain-based digital identities, individuals without traditional identification documents can establish verifiable digital identities, enabling them to access banking services, loans, and participate in the formal economy. Additionally, blockchain-based remittance services can offer faster, cheaper, and more secure cross-border transactions, benefiting migrant workers and their families.
6. Tokenization and asset ownership: Blockchain allows for the tokenization of physical and digital assets, representing ownership or value in a digital form. This enables fractional ownership, liquidity, and tradability of assets that were previously illiquid or restricted to a limited group of investors. Tokenization opens up opportunities for real estate investments, art, intellectual property rights, and other assets, creating more accessible and inclusive investment markets.
7. Economic empowerment and decentralized governance: Blockchain-based platforms can empower individuals by providing them with control over their data, digital assets, and financial transactions. Through decentralized governance mechanisms, participants can have a say in the decision-making processes of blockchain networks and protocols, fostering a more democratic and inclusive economy. This empowerment can lead to increased economic opportunities, innovation, and collaboration.
It is important to note that while Ethereum and blockchain offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges to overcome, including scalability, regulatory frameworks, energy consumption, and interoperability. However, the potential of Ethereum and blockchain technology to transform the economy and drive innovation is significant, and their continued development and adoption are expected to reshape various sectors and create new opportunities in the global economy.
Also read: How Does Ethereum In Casino Work?
Top 10 Ethereum Blockchain Innovations Driving Adoption and Growth
Sure, here is an article about the top 10 Ethereum blockchain innovations driving adoption and growth:
Top 10 Ethereum Blockchain Innovations Driving Adoption and Growth
Ethereum is a blockchain platform that allows for the creation of decentralized applications (Dapps). Dapps are applications that run on a peer-to-peer network and are not controlled by any central authority. This makes them ideal for applications that require trustless and secure transactions, such as financial services and supply chain management.
In recent years, Ethereum has seen a surge in adoption and growth. This is due in part to the many innovations that have been developed on the platform. Here are the top 10 Ethereum blockchain innovations driving adoption and growth:
- Smart contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are stored on the blockchain. They can be used to automate a wide range of transactions, such as payments, loans, and insurance. Smart contracts are one of the most important innovations on Ethereum, as they allow for trustless and secure transactions without the need for a third party.

- Decentralized finance (DeFi): DeFi is a financial system that is built on top of blockchain technology. It allows for people to access financial services without the need for a traditional financial institution. DeFi is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the blockchain industry, and it is being used for a wide range of applications, such as lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs): NFTs are digital assets that are unique and cannot be replaced. They are often used to represent ownership of digital artworks, collectibles, and in-game items. NFTs have exploded in popularity in recent years, and they are now being used in a wide range of industries, including gaming, art, and finance.

- Consensus mechanisms: Consensus mechanisms are algorithms that are used to reach agreement on the state of the blockchain. The most common consensus mechanism on Ethereum is proof-of-work (PoW), but there are a number of other consensus mechanisms being developed, such as proof-of-stake (PoS) and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS). The consensus mechanism that is used can have a significant impact on the performance and security of the blockchain.
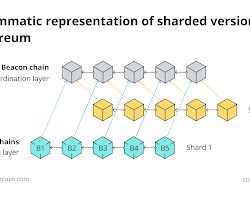
- Sharding: Sharding is a technique that can be used to improve the scalability of blockchains. By dividing the blockchain into smaller pieces, called shards, it is possible to process more transactions per second. Sharding is still in development, but it has the potential to make Ethereum much more scalable.
- Privacy features: Ethereum is not a privacy-focused blockchain, but there are a number of projects that are working on developing privacy features for the platform. These features could be used to protect user data and to make Ethereum more suitable for applications that require a high degree of privacy.
- Scalability solutions: Ethereum is facing scalability challenges, as the network can only process a limited number of transactions per second. A number of scalability solutions are being developed, such as sharding, state channels, and plasma. These solutions could help to make Ethereum more scalable and able to handle the increasing demand for transactions.
- Enterprise adoption: Ethereum is increasingly being adopted by businesses and organizations. A number of large companies are now using Ethereum for a variety of applications, such as supply chain management, financial services, and insurance. Enterprise adoption is one of the key drivers of growth for Ethereum, and it is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
- Developer community: Ethereum has a large and active developer community. This community is responsible for developing new applications and features for the platform. The developer community is one of the main strengths of Ethereum, and it is essential for the continued growth and development of the platform.

- Marketing and awareness: Ethereum is still a relatively young platform, and it is not as well-known as some other blockchain platforms. However, there is a growing awareness of Ethereum, and this is being driven by a number of factors, such as the increasing adoption of DeFi and NFTs. Marketing and awareness are essential for the continued growth of Ethereum, and it is expected that the platform will become more widely known in the years to come.
Risks associated with Ethereum and Blockchain
While Ethereum and blockchain technology offer numerous benefits and opportunities, there are several risks and challenges that should be considered. Here are some of the key risks associated with Ethereum and blockchain:
1. Security vulnerabilities: While blockchain is touted for its security, no system is entirely immune to vulnerabilities. Smart contracts deployed on Ethereum are not immune to bugs or coding errors, and if exploited, these vulnerabilities can lead to financial losses or other detrimental effects. The infamous DAO hack in 2016, which exploited a vulnerability in a smart contract, resulted in the theft of millions of dollars’ worth of Ether. Ongoing audits, code reviews, and security best practices are necessary to minimize such risks.
2. Regulatory uncertainty: The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving and varies across different jurisdictions. Regulatory actions, such as restrictive legislation, taxation policies, or bans, can significantly impact the usability and adoption of Ethereum and blockchain technology. Uncertainty around regulatory compliance and potential legal repercussions can deter businesses and individuals from fully embracing blockchain solutions.
3. Scalability limitations: Scalability remains a challenge for Ethereum and other blockchain networks. As the number of participants and transactions increases, the network can face congestion and slower transaction processing times. This limitation hampers the scalability of decentralized applications and can hinder the widespread adoption of Ethereum in high-demand use cases, such as global payment systems or internet-scale applications. Efforts like Ethereum 2.0 aim to address scalability through the introduction of sharding and a transition to Proof-of-Stake consensus.
4. Interoperability challenges: Interoperability refers to the ability of different blockchains and systems to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. The lack of standardization and interoperability protocols can create siloed blockchain networks, limiting the potential benefits of a decentralized ecosystem. Interoperability challenges can hinder the efficient transfer of assets, data, and value between different blockchains and ecosystems, reducing the overall utility and adoption of Ethereum and blockchain technology.
5. Energy consumption: The energy consumption associated with blockchain, particularly the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism used by Ethereum, has raised concerns about its environmental impact. The computational power required for mining and validating transactions can be energy-intensive, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Efforts to transition Ethereum to a more energy-efficient consensus mechanism, such as Proof-of-Stake, are underway to address these concerns.
6. User error and irreversibility: Blockchain transactions, once confirmed and added to the blockchain, are nearly immutable and irreversible. While this feature enhances security and prevents fraudulent activities, it can also be a risk if users make mistakes or encounter fraudulent transactions. Accidental loss of private keys, sending funds to the wrong address, or falling victim to phishing attacks can result in permanent loss of assets. Users must exercise caution and follow best practices to safeguard their private keys and ensure the accuracy of transactions.
7. Lack of privacy: While blockchain transactions are transparent, they are also pseudonymous, meaning that transactions are associated with cryptographic addresses rather than real-world identities. However, sophisticated analysis techniques can potentially deanonymize participants and trace transactions, compromising privacy. Privacy-enhancing technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs and secure multiparty computation, are being developed to address these concerns. However, ensuring privacy without compromising transparency remains a challenge.
8. Technological obsolescence: Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, and new advancements could make existing implementations, including Ethereum, obsolete or less competitive. Technological advancements, protocol upgrades, or the emergence of new blockchain platforms may impact the adoption and value proposition of Ethereum. Staying abreast of technological developments and ensuring adaptability to changing landscapes is crucial to mitigate the risk of technological obsolescence.
As with any emerging technology, it is important to assess and manage these risks. Robust security measures, regulatory compliance, ongoing research and development efforts, and user education are crucial for minimizing risks and maximizing the potential benefits of Ethereum and blockchain technology.
Also read: Your Ultimate Guide To Ethereum RPC Nodes
Future of Ethereum and Blockchain
The future of Ethereum and blockchain technology holds immense potential for transformative impact across various industries and sectors. Here are some key areas that highlight the potential future developments:
1. Ethereum 2.0: Ethereum is undergoing a significant upgrade known as Ethereum 2.0 or Eth2. This upgrade aims to address scalability, energy efficiency, and security concerns associated with the current Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. Ethereum 2.0 introduces Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus, shard chains for scalability, and a new virtual machine. This upgrade is expected to enhance the scalability and efficiency of the Ethereum network, opening doors to a broader range of use cases and facilitating increased adoption.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi has emerged as a prominent sector within the Ethereum ecosystem. DeFi applications aim to recreate traditional financial systems in a decentralized and trustless manner using smart contracts. With DeFi, individuals can access lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services without relying on intermediaries. The future of Ethereum and blockchain is likely to see further growth and innovation in the DeFi space, potentially transforming traditional financial systems and increasing financial inclusion.
3. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs have gained significant attention and adoption, enabling unique digital ownership and representation of assets. NFTs are tokens that represent ownership or proof of authenticity of digital or physical items such as art, music, collectibles, and virtual real estate. Ethereum has been a key platform for NFT development, and the future of Ethereum is expected to witness continued growth in NFTs, with advancements in areas like NFT marketplaces, intellectual property rights, and gamification.
4. Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions: Interoperability is a crucial aspect for the future of blockchain technology. As the number of blockchains increases, the ability to communicate and exchange value seamlessly between different blockchain networks becomes vital. Solutions like cross-chain bridges, interoperability protocols, and standardized frameworks are being developed to enable interoperability and create a connected blockchain ecosystem. The future of Ethereum and blockchain will likely see advancements in interoperability, facilitating efficient asset transfers and collaborations between different blockchains.
5. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Several central banks worldwide are exploring the concept of issuing their digital currencies using blockchain technology. These Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) aim to provide a digital form of fiat currency while leveraging the benefits of blockchain, such as transparency, security, and programmability. Ethereum has been considered as a potential platform for CBDC development, and the future may witness the integration of Ethereum or Ethereum-based solutions into national digital currency initiatives.
6. Enterprise Adoption: Blockchain technology has been gaining attention from enterprises across industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, energy, and more. As the technology matures and scalability improves, Ethereum and blockchain are likely to witness increased enterprise adoption. Enterprises can leverage blockchain for enhanced transparency, traceability, and efficiency in their operations, leading to cost savings and improved trust among stakeholders.
7. Sustainability and Green Initiatives: As the environmental impact of blockchain technology becomes more apparent, efforts are being made to address sustainability concerns. The future of Ethereum and blockchain will likely focus on enhancing energy efficiency, exploring alternative consensus mechanisms, and integrating sustainable practices. Transitioning to Proof-of-Stake consensus in Ethereum 2.0 is one such step towards reducing energy consumption. Additionally, research and development efforts are ongoing to optimize energy usage and improve the environmental sustainability of blockchain networks.
8. Regulation and Standards: With the increasing adoption of blockchain technology, governments and regulatory bodies are actively working on frameworks and regulations to govern its usage. The future of Ethereum and blockchain will likely witness the development of clearer regulations and standards to ensure consumer protection, prevent fraud, and foster responsible innovation. Regulatory clarity is crucial to encourage mainstream adoption and mitigate risks associated with blockchain technology.
It’s important to note that the future of Ethereum and blockchain technology is dynamic and subject to rapid innovation and development. New technological advancements, unforeseen challenges, and market forces will shape the trajectory of Ethereum and blockchain in the coming years. However, the potential for transformative impact across various sectors and industries remains significant, making Ethereum and blockchain technology an integral part of the digital future.




























































