Top 10 Financial Services That Are Revolutionized Blockchain

Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has gained significant attention and popularity in recent years. It is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that allows secure and transparent recording of transactions and information across multiple parties. The concept of blockchain was introduced in 2008 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, as the underlying technology behind the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. However, its potential applications extend far beyond just cryptocurrencies.
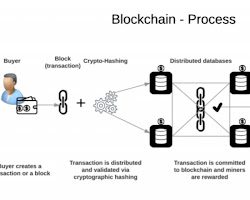
At its core, a blockchain is a chain of blocks that contain a series of data or transactions. Each block is linked to the previous block through cryptographic hashes, forming a chronological and immutable chain. This linkage ensures the integrity and security of the information stored within the blockchain. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or tamper with the data, making it highly resistant to fraud and unauthorized modifications.
One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single entity or authority has control over the data, a blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network. This means that multiple participants, known as nodes, collectively maintain and validate the blockchain. Each node stores a complete copy of the blockchain and participates in the consensus process to agree on the validity of transactions and blocks.
Consensus mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of the blockchain. Various consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), are employed to ensure that the majority of nodes in the network agree on the state of the blockchain. These algorithms require nodes to solve complex mathematical problems or stake a certain amount of cryptocurrency to validate transactions and create new blocks.
The decentralized and transparent nature of blockchain provides several benefits. First and foremost, it eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or clearinghouses, in transactions, resulting in faster and more efficient processes. It also reduces costs by eliminating the fees associated with intermediaries and streamlines record-keeping by maintaining a single, shared ledger accessible to all participants.
Furthermore, blockchain offers enhanced security. The use of cryptographic algorithms ensures that the data stored within the blockchain is secure and tamper-proof. Additionally, the distributed nature of the network makes it resistant to single points of failure and cyberattacks. Any attempt to tamper with the data would require significant computational power and would need to simultaneously compromise a majority of the nodes in the network, making it highly impractical.
Blockchain technology has expanded beyond cryptocurrencies to find applications in various industries. It has shown immense potential in supply chain management, where it can enhance traceability and transparency by recording the movement of goods from their origin to the end consumer. In the healthcare sector, blockchain can securely store and share patient records, ensuring privacy and accuracy while enabling interoperability between different healthcare providers. It can also be used for voting systems, intellectual property rights management, identity verification, and more.
Despite its many advantages, blockchain faces challenges and limitations. Scalability is a significant concern, as the consensus mechanisms and the need for all nodes to store a copy of the blockchain can lead to performance issues. Efforts are being made to develop solutions like sharding and off-chain transactions to address these concerns. Additionally, regulatory and legal frameworks surrounding blockchain are still evolving, and issues related to privacy, data protection, and governance need to be carefully addressed.
In conclusion, blockchain is a groundbreaking technology that enables secure, transparent, and decentralized record-keeping and transactions. Its potential to disrupt multiple industries and transform existing processes is immense. While there are challenges to overcome, the ongoing development and adoption of blockchain are likely to reshape various sectors, ushering in a new era of trust, efficiency, and innovation.
Importance of Financial Services by Blockchain for the Economy
The importance of financial services provided by blockchain for the economy cannot be understated. Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize and improve many aspects of the financial industry, offering numerous benefits to businesses, individuals, and the overall economy. Here are several key ways in which blockchain-based financial services contribute to the economy:
1. Enhanced Security: Traditional financial systems often face security vulnerabilities due to centralized data storage and reliance on intermediaries. Blockchain addresses these concerns by employing robust cryptographic algorithms and decentralized consensus mechanisms. This ensures the security and integrity of financial transactions, protecting against fraud, hacking, and unauthorized access. By reducing security risks, blockchain enhances trust in financial services and promotes economic stability.
2. Improved Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines financial processes by eliminating intermediaries and reducing the need for manual reconciliation and paperwork. It facilitates faster settlement of transactions, eliminating delays caused by complex clearance procedures. Real-time verification and validation of transactions on the blockchain remove the need for time-consuming manual verification, resulting in quicker and more efficient financial services. This efficiency translates into cost savings for businesses and individuals alike.
3. Cost Reduction: The traditional financial system often involves high fees and operational costs associated with intermediaries, such as banks and payment processors. Blockchain technology eliminates the need for intermediaries, enabling peer-to-peer transactions and reducing transaction fees significantly. Additionally, automated smart contracts on blockchain platforms can eliminate the need for costly third-party intermediaries in various financial agreements, such as escrow services, loans, and insurance claims. These cost reductions benefit both businesses and consumers, freeing up resources for investment and spending.
4. Financial Inclusion: Blockchain has the potential to address the issue of financial exclusion by providing access to financial services to unbanked or underbanked populations. With a smartphone and internet access, individuals can participate in blockchain-based financial networks and access various financial services, such as payments, remittances, lending, and savings. This inclusion empowers individuals, promotes economic growth, and reduces poverty by enabling greater participation in the formal economy.
5. Transparent and Auditable Transactions: Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology provides transparency and immutability, allowing anyone to view transaction histories while ensuring data integrity. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and increases accountability. It also simplifies auditing processes for regulatory compliance, reducing the administrative burden on financial institutions and enhancing trust in the financial system. Enhanced transparency can attract more investors and foster economic growth by providing a clear view of financial activities.
6. Cross-Border Transactions: Blockchain has the potential to simplify and accelerate cross-border transactions, which are often slow, expensive, and prone to errors. By removing intermediaries and facilitating direct peer-to-peer transactions, blockchain-based financial services can enable faster settlement, reduce foreign exchange costs, and improve liquidity. This has significant implications for global trade, remittances, and international investment, promoting economic integration and stimulating economic growth.
7. Innovation and Economic Growth: Blockchain technology fosters innovation by enabling the development of new financial products and services. It provides a platform for the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts, opening avenues for automated financial agreements and programmable money. This innovation drives entrepreneurship, attracts investment, and fuels economic growth. Moreover, blockchain can facilitate crowdfunding and access to capital for startups and small businesses, promoting economic development and job creation.
In summary, blockchain-based financial services offer enhanced security, efficiency, cost reduction, financial inclusion, transparency, and cross-border transaction capabilities. By leveraging these benefits, the economy can experience improved trust, reduced costs, increased financial participation, accelerated transactions, and enhanced innovation. As blockchain continues to evolve and mature, its impact on the financial services sector and the broader economy is expected to be profound, transforming the way financial transactions are conducted and driving positive economic outcomes.
Also read: RippleNet to Use Open Network And Blockchain to Enable Financial Services
Top 10 Financial Services by Blockchain
Blockchain technology is rapidly transforming the financial services industry, with a wide range of applications being explored. Here are some of the top 10 financial services that are being revolutionized by blockchain:
- Payments and remittances. Blockchain can be used to create more efficient and secure payment systems. For example, blockchain-based payments can be processed instantly and with no fees, and they can also be tracked in real time. This makes them ideal for international remittances, where speed and transparency are essential.
- Clearance and settlement. Blockchain can also be used to streamline the clearance and settlement process for financial transactions. This can help to reduce costs and risks, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of the process.
- Trade finance. Blockchain can be used to create more secure and efficient trade finance solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods and payments, and it can also be used to verify the authenticity of documents. This can help to reduce fraud and risk, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of trade finance transactions.
- Asset management. Blockchain can be used to create more secure and transparent asset management solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to track the ownership and movement of assets, and it can also be used to provide investors with real-time information about their investments. This can help to reduce risk and fraud, and it can also improve the efficiency of asset management processes.
- Identity verification. Blockchain can be used to create more secure and reliable identity verification solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to store and verify personal data, such as passports and driver’s licenses. This can help to reduce fraud and identity theft, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of identity verification processes.
- Insurance. Blockchain can be used to create more efficient and secure insurance solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to track claims and payments, and it can also be used to verify the authenticity of insurance policies. This can help to reduce fraud and risk, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of insurance claims processing.
- Compliance. Blockchain can be used to create more efficient and secure compliance solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to store and track compliance data, such as financial transactions and customer information. This can help to reduce risk and errors, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of compliance processes.

- Regulatory compliance. Blockchain can be used to create more efficient and secure regulatory compliance solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to store and track regulatory data, such as financial transactions and customer information. This can help to reduce risk and errors, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of regulatory compliance processes.
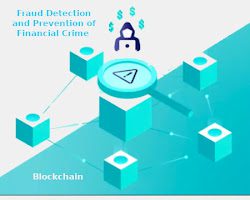
- Fraud detection and prevention. Blockchain can be used to create more efficient and secure fraud detection and prevention solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to track transactions and identify patterns of suspicious activity. This can help to reduce fraud and risk, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of fraud detection and prevention processes.
- Supply chain management. Blockchain can be used to create more efficient and secure supply chain management solutions. For example, blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods and materials, and it can also be used to verify the authenticity of products. This can help to reduce fraud and risk, and it can also improve the speed and efficiency of supply chain management processes.
These are just a few of the many ways that blockchain is being used to revolutionize the financial services industry. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and disruptive applications in the years to come.
Benefits of Blockchain Financial Services
Blockchain financial services offer a wide range of benefits that can positively impact businesses, individuals, and the overall financial ecosystem. Here are several key advantages of utilizing blockchain technology in financial services:
1. Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology incorporates advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and data. The decentralized nature of blockchain, where multiple nodes maintain and validate the ledger, makes it highly resistant to hacking and tampering. Each transaction is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating an immutable and transparent audit trail. This level of security significantly reduces the risk of fraud, identity theft, and unauthorized access, instilling trust in financial transactions.
2. Improved Efficiency: Traditional financial processes can be time-consuming and involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and inefficiencies. By leveraging blockchain, financial services can achieve faster settlement times, reduced paperwork, and streamlined processes. Blockchain enables near real-time verification and validation of transactions, eliminating the need for manual reconciliation and minimizing human errors. Automated smart contracts on blockchain platforms can facilitate self-executing financial agreements, further enhancing efficiency and reducing administrative overhead.
3. Cost Reduction: The elimination of intermediaries in blockchain-based financial services can lead to significant cost savings. Traditional financial transactions often incur fees associated with banks, payment processors, and other intermediaries. By conducting transactions directly on the blockchain, these fees can be greatly reduced or even eliminated. Additionally, the automation of processes through smart contracts reduces the need for third-party intermediaries in areas such as insurance claims, loans, and trade finance, resulting in further cost reductions for businesses and consumers.
4. Financial Inclusion: One of the transformative aspects of blockchain financial services is its potential to foster financial inclusion. Many individuals around the world, particularly in developing regions, lack access to traditional banking services. Blockchain technology allows for the creation of digital wallets and decentralized financial networks, enabling individuals to participate in financial services without the need for a traditional bank account. This opens up avenues for payments, remittances, loans, and savings for the unbanked and underbanked populations, promoting economic growth and reducing poverty.
5. Transparency and Auditability: Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology provides transparency and immutability of transaction data. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants, enhancing transparency and reducing the potential for fraudulent activities. This transparency, combined with the ability to trace and verify transactions, simplifies auditing processes for regulatory compliance. Regulators can easily access and review transaction histories, ensuring adherence to financial regulations and promoting accountability within the financial ecosystem.
6. Cross-Border Transactions: Traditional cross-border transactions are often complex, involving multiple intermediaries, high fees, and lengthy settlement times. Blockchain financial services have the potential to simplify and expedite cross-border transactions. By eliminating intermediaries and enabling peer-to-peer transactions, blockchain can reduce costs, enhance liquidity, and expedite settlement times. This can have a significant impact on global trade, remittances, and cross-border investments, facilitating economic integration and fostering international cooperation.
7. Innovation and New Business Models: Blockchain technology has the capacity to drive innovation in the financial sector. The ability to create decentralized applications (DApps) and programmable smart contracts opens up new possibilities for financial products and services. Blockchain-based platforms enable the development of innovative solutions such as decentralized lending, crowdfunding, asset tokenization, and decentralized exchanges. These innovations can democratize access to capital, promote entrepreneurship, and fuel economic growth by providing new avenues for fundraising and investment.
8. Data Privacy and Control: In traditional financial systems, individuals often have limited control over their financial data, and there are concerns about privacy and data breaches. Blockchain allows individuals to have greater control over their personal data by employing cryptographic techniques to secure and control access to information. Users can decide which information to share and with whom, enhancing privacy and giving individuals more ownership and control over their financial information.
These benefits of blockchain financial services contribute to a more secure, efficient, inclusive, and transparent financial ecosystem. By reducing costs, eliminating intermediaries, and fostering innovation, blockchain technology has the potential to unlock economic opportunities and drive positive change in various industries, ultimately leading to sustainable economic growth.
Also read: South Korea’s NH Bank Dives into the Blockchain Financial Services Sector
Future of Blockchain Financial Services
The future of blockchain financial services holds great potential for transforming the way financial transactions are conducted, managed, and recorded. Here are several key trends and possibilities that may shape the future of blockchain financial services:
1. Mainstream Adoption: As blockchain technology continues to mature and gain wider recognition, we can expect increased adoption of blockchain-based financial services by mainstream financial institutions. Traditional banks, payment processors, and other financial intermediaries are exploring ways to leverage blockchain to enhance their operations, reduce costs, and improve security. Collaborations and partnerships between traditional financial institutions and blockchain startups are likely to increase, facilitating the integration of blockchain into existing financial infrastructure.
2. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Central banks worldwide are actively exploring the concept of CBDCs, which are digital representations of fiat currencies issued and controlled by central authorities. Blockchain technology is well-suited for CBDC implementation, as it provides secure and transparent transactions while enabling central banks to maintain control over the monetary system. CBDCs can streamline payments, enhance financial inclusion, and provide a programmable and interoperable foundation for the future of money.
3. Interoperability and Standardization: As blockchain networks continue to proliferate, interoperability and standardization will become crucial for seamless communication and exchange of value between different blockchain platforms. Efforts are underway to develop protocols and frameworks that facilitate interoperability, allowing different blockchains to interact and share data securely. This interoperability will unlock new possibilities for cross-chain transactions, asset transfers, and the creation of interconnected financial ecosystems.
4. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Evolution: Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has emerged as one of the most significant use cases for blockchain in the financial sector. DeFi platforms offer a range of financial services, including lending, borrowing, decentralized exchanges, and asset management, without the need for intermediaries. The future of blockchain financial services will likely see the continued growth and maturation of DeFi, with increased adoption, improved user experience, and enhanced security measures.
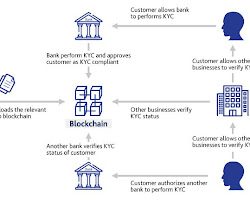
5. Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance: The regulatory landscape for blockchain financial services is still evolving. Regulators worldwide are working to develop frameworks that address the unique challenges and opportunities presented by blockchain technology. Clear regulations surrounding digital assets, smart contracts, and identity verification will help foster innovation while ensuring consumer protection and compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. Regulatory clarity will be crucial for broader adoption of blockchain financial services.
6. Scalability and Performance Improvements: Blockchain technology faces scalability challenges as the number of transactions and participants on a network grows. To overcome this hurdle, researchers and developers are exploring various solutions such as layer 2 protocols, sharding, and consensus algorithm optimizations. These advancements aim to enhance blockchain scalability and improve transaction throughput without compromising security or decentralization. As scalability improves, blockchain financial services will be able to handle a larger volume of transactions, facilitating mass adoption.
7. Integration with Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI): The convergence of blockchain with other emerging technologies like IoT and AI holds significant potential for the future of blockchain financial services. Combining blockchain with IoT devices can enable secure and transparent machine-to-machine transactions, automated supply chain management, and efficient tracking of physical assets. AI algorithms can leverage blockchain’s transparent and auditable data to enhance risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized financial services.
8. Green and Sustainable Blockchain Solutions: Blockchain networks, particularly those that rely on Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, consume a significant amount of energy. In the future, there will be a growing focus on developing more energy-efficient and sustainable blockchain solutions. Transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS) or other energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, along with advancements in blockchain infrastructure and optimization techniques, will help mitigate the environmental impact and create more sustainable blockchain financial services.
In summary, the future of blockchain financial services is likely to witness increased mainstream adoption, the emergence of CBDCs, improved interoperability, continued growth of DeFi, evolving regulatory frameworks, scalability improvements, integration with IoT and AI, and a focus on sustainability. These trends and developments have the potential to reshape the financial industry, promoting efficiency, transparency, financial inclusion, and innovation while addressing existing challenges and unlocking new economic opportunities.
This is why Decentralised banking is so important and it’s going to take the World by storm! #ReDeFi MainNet’s launch by Bank Account Based Blockchain, #BABB will revolutionise The Global Financial Services Industry forever! Imagine one app holding UK 🇬🇧, EU and US money accounts… https://t.co/OpazjzuX1T pic.twitter.com/AZ4vZQU42k
— Ⓑ Tuan Ⓑ (@uk_tuan) June 30, 2023




























































