Top 10 NFTs Use Cases To Make Real World Experiences Richer

Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are a type of digital asset that represent ownership or proof of authenticity of a unique item or piece of content using blockchain technology. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and can be exchanged on a one-to-one basis, NFTs are indivisible and cannot be exchanged on a like-for-like basis.
NFTs leverage the power of blockchain, a decentralized and distributed ledger technology that ensures transparency, security, and immutability. Blockchain technology allows for the creation of a digital certificate of authenticity, which verifies the ownership and provenance of a specific item or piece of content. This certificate is stored on the blockchain and can be publicly accessed, providing a transparent record of ownership.
One of the key features of NFTs is their uniqueness. Each NFT is distinct and can represent a wide range of digital or physical items, such as art, music, videos, virtual real estate, collectibles, in-game items, and more. NFTs provide a way to establish and verify ownership of these items in the digital realm, where duplication and counterfeiting are common concerns.
The uniqueness and scarcity of NFTs contribute to their value. Because there is only one official, verifiable version of a particular NFT, it can be considered rare and valuable. The value of NFTs is often determined by factors such as the reputation and popularity of the creator, the demand for the item or content, and the perceived uniqueness or aesthetic appeal.
NFT transactions are typically conducted using cryptocurrencies, most commonly Ethereum, due to its robust smart contract capabilities. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions coded into them. They facilitate the automatic transfer of ownership and enforce royalty payments or other financial arrangements between the creator and subsequent buyers or sellers of an NFT.
Creators or artists often release NFTs through digital marketplaces or platforms specifically designed for buying, selling, and trading these digital assets. These platforms provide a marketplace for creators to showcase and sell their work directly to collectors and enthusiasts. Some popular NFT marketplaces include OpenSea, Rarible, SuperRare, and NBA Top Shot.
Another significant aspect of NFTs is the potential for creators to earn royalties from secondary market transactions. When an NFT is sold or traded on a secondary market, the creator can include a royalty fee in the smart contract, ensuring that they receive a percentage of the subsequent sales. This feature allows artists to continue benefiting financially from the increasing value and demand for their work even after the initial sale.
However, it is important to note that NFTs have generated both excitement and controversy. Proponents argue that NFTs empower artists and creators by providing them with new revenue streams, increased control over their work, and the ability to establish a direct relationship with their audience. Critics express concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology, the potential for fraud or copyright infringement, and the volatility and speculative nature of the NFT market.
In conclusion, NFTs are digital assets that leverage blockchain technology to establish ownership and authenticity of unique items or content. They have gained popularity as a means for artists, creators, and collectors to participate in the digital art and collectibles market, opening up new possibilities for monetization and ownership in the digital age.
Also read: NFT Investment in 2023: Everything You Need to Know
Importance of NFTs for the Economy
NFTs (Non-fungible tokens) have emerged as a significant development with the potential to impact the economy in various ways. Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of NFTs for the economy:
1. Empowering Creators and Artists: NFTs provide creators and artists with new avenues for monetizing their work. By tokenizing their creations as NFTs, they can directly sell digital art, music, videos, and other unique digital content to collectors and enthusiasts. This allows creators to bypass traditional intermediaries and retain a larger share of the revenue generated from their work.
2. Establishing Ownership and Authenticity: NFTs utilize blockchain technology to establish verifiable ownership and provenance of digital assets. This feature has significant implications for the economy, as it addresses the challenges of digital ownership and counterfeiting. NFTs enable creators, collectors, and businesses to trade and transfer unique digital assets with confidence, increasing trust and transparency in digital transactions.
3. Expanding Digital Collectibles Market: NFTs have brought about a resurgence of interest in digital collectibles. Collectors can now own and trade unique digital items such as virtual trading cards, virtual real estate, in-game assets, and more. This market expansion creates economic opportunities for collectors, developers, and platforms that facilitate the buying and selling of these digital collectibles.
4. Enabling Fractional Ownership and Investment: NFTs can be divided into smaller fractional units, enabling shared ownership of high-value assets. This fractional ownership model opens up possibilities for new investment opportunities. Investors can purchase fractions of valuable NFTs, allowing them to participate in the potential appreciation of these assets, similar to owning shares in a company or real estate.
5. Royalties and Residual Income: NFTs have introduced the concept of royalties and residual income for creators. Through smart contracts embedded within NFTs, creators can receive a percentage of subsequent sales whenever their NFTs are resold on secondary markets. This ongoing revenue stream provides creators with long-term financial benefits and incentivizes them to continue producing valuable content.
6. Supporting Creative Industries: The creative industries, including art, music, literature, gaming, and entertainment, play a significant role in the global economy. NFTs provide a new revenue stream and economic ecosystem for these industries. Artists and creators can leverage NFTs to reach a global audience, monetize their work directly, and develop stronger connections with their fans and supporters.
7. Promoting Innovation and Collaboration: NFTs encourage innovation and collaboration among creators, developers, and entrepreneurs. The ability to tokenize and trade digital assets fosters an environment where creators can experiment, collaborate, and build upon each other’s work. This cross-pollination of ideas and assets can lead to new forms of creativity, unique collaborations, and the development of novel digital experiences.
8. Impact on Traditional Markets: NFTs have the potential to disrupt traditional markets, such as the art market, by introducing new models of ownership and distribution. The direct-to-consumer nature of NFT transactions reduces the reliance on galleries, auction houses, and intermediaries. This can democratize access to art and other digital assets, allowing emerging artists and creators to gain recognition and generate revenue without the need for extensive networks or gatekeepers.
While the impact of NFTs on the economy is still evolving and subject to ongoing debate, their potential to reshape digital ownership, empower creators, and create new economic opportunities is undeniable. As the technology matures and adoption increases, NFTs are likely to have a lasting impact on various industries and contribute to the broader digital economy.
Also read: Top 5 Business Use Cases For NFTs In The Coming Years
Top 10 NFT Use Cases to make Real World Experiences Richer
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets that can represent anything from art and collectibles to real estate and in-game items. They are stored on a blockchain, which makes them secure and unforgeable.
NFTs have the potential to make real-world experiences richer in a number of ways. Here are 10 of the most promising use cases:
- Art and collectibles: NFTs have already been used to sell some of the most expensive pieces of digital art ever created. They can also be used to collect rare collectibles, such as sports trading cards or virtual pets.

- Music: NFTs can be used to sell music in a way that gives artists more control over their work. They can also be used to create limited-edition albums or singles, or to sell tickets to exclusive concerts.

- Event ticketing: NFTs can be used to create more secure and tamper-proof event tickets. They can also be used to sell tickets to exclusive events or to create VIP experiences.

- Virtual real estate: NFTs can be used to buy, sell, and trade virtual real estate in online worlds, such as Decentraland and The Sandbox. This could open up new opportunities for businesses and individuals to own and develop virtual property.

- Gaming: NFTs can be used to create in-game items that have real-world value. This could lead to a more immersive and engaging gaming experience, as well as new opportunities for players to earn money.
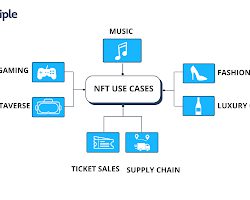
- Fashion: NFTs can be used to create digital fashion items that can be worn in virtual worlds. This could lead to a new way for people to express themselves and to connect with others.
- Supply chain: NFTs can be used to track the provenance of goods and to ensure that they are authentic. This could be used to improve the efficiency of supply chains and to reduce fraud.

- Education: NFTs can be used to create digital certificates and diplomas that are more secure and tamper-proof than traditional certificates. This could make it easier for employers to verify the qualifications of job candidates.

- Charity: NFTs can be used to raise money for charity in a more transparent and efficient way. They can also be used to create exclusive experiences for donors.
- Web3 identity: NFTs can be used to create digital identities that are more secure and portable than traditional identities. This could make it easier for people to interact with online services and to protect their privacy.
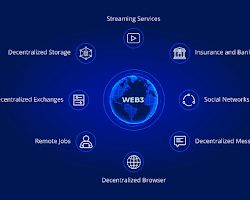
These are just a few of the many potential use cases for NFTs. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative and exciting ways to use NFTs to make real-world experiences richer.
Benefits of using NFTs
The use of NFTs (Non-fungible tokens) brings several benefits across various domains. Here are the key advantages of using NFTs:
1. Proof of Ownership and Authenticity: NFTs utilize blockchain technology to establish verifiable ownership and authenticity of digital assets. This feature is particularly valuable in the digital realm, where duplication and counterfeit items are common. NFTs provide a transparent and immutable record of ownership, giving confidence to buyers and collectors that they own a unique and genuine asset.
2. Direct Monetization for Creators: NFTs empower creators, artists, musicians, and other content creators to directly monetize their work. By tokenizing their creations as NFTs, creators can sell them directly to collectors and enthusiasts without the need for intermediaries such as galleries, agents, or record labels. This direct-to-consumer model allows creators to retain a larger share of the revenue generated from their work.
3. New Revenue Streams: NFTs introduce new revenue streams for creators. Through the use of smart contracts embedded within NFTs, creators can receive royalties or a percentage of subsequent sales whenever their NFTs are resold on secondary markets. This ongoing revenue stream provides creators with the potential for long-term financial benefits and incentivizes them to continue producing valuable content.
4. Fractional Ownership and Investment Opportunities: NFTs can be divided into smaller fractional units, enabling shared ownership of high-value assets. This fractional ownership model allows investors to purchase fractions of valuable NFTs, enabling broader participation and investment opportunities. Fractional ownership makes it possible for individuals with limited financial means to invest in high-value assets and potentially benefit from their appreciation.
5. Transparency and Security: NFTs leverage blockchain technology, which provides transparency, security, and immutability. Every transaction and ownership transfer associated with an NFT is recorded on the blockchain, creating a public and transparent ledger. This transparency ensures that the ownership history and provenance of an NFT can be easily verified, reducing the risk of fraud or counterfeit assets.
6. Increased Access and Democratization: NFTs have the potential to democratize access to digital assets, including art, music, virtual real estate, and more. By removing geographical and institutional barriers, NFTs enable creators from diverse backgrounds and regions to showcase and sell their work to a global audience. Likewise, collectors and enthusiasts gain access to a wider range of unique digital assets that may have been previously inaccessible.
7. Enhanced Fan Engagement and Interaction: NFTs offer new ways for creators to engage with their audience and fans. Creators can use NFTs to offer exclusive content, limited editions, or special experiences to their most dedicated supporters. NFTs can also serve as a membership or loyalty mechanism, granting access to perks, events, or additional content. This strengthens the relationship between creators and their community, fostering deeper engagement and support.
8. Preservation of Digital Art and Cultural Heritage: NFTs provide a means to preserve and protect digital art and cultural heritage. The blockchain-based provenance and immutability of NFTs ensure that the history and authenticity of digital artworks are safeguarded. Additionally, NFTs can include embedded metadata, descriptions, and contextual information about the artwork, facilitating the preservation of the artist’s intent and cultural significance.
9. Innovation and Collaboration: NFTs encourage innovation and collaboration among creators, developers, and entrepreneurs. The ability to tokenize and trade digital assets fosters an environment where creators can experiment, collaborate, and build upon each other’s work. This cross-pollination of ideas and assets can lead to new forms of creativity, unique collaborations, and the development of novel digital experiences.
Also read: Top 10 Gaming Assets Pave The Way For NFT Adoption
Future of NFTs
The future of NFTs (Non-fungible tokens) is a topic of great interest and speculation, as this technology continues to evolve and gain traction. Here are some potential trends and possibilities that could shape the future of NFTs:
1. Expansion of Use Cases: Currently, NFTs are primarily associated with digital art and collectibles. However, the future of NFTs holds the potential for their application in various industries and domains. NFTs could be utilized in areas such as real estate, intellectual property rights, ticketing, virtual and augmented reality experiences, virtual fashion, supply chain verification, and more. As the technology matures, we can expect to see a broader range of use cases emerge.
2. Integration with the Physical World: While NFTs are predominantly digital assets, there is a growing interest in bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds. Some projects are exploring the concept of tokenizing physical assets, such as real estate properties, luxury goods, or rare physical collectibles, through the use of NFTs. This integration would provide a seamless way to establish ownership, provenance, and transferability of physical assets using blockchain technology.
3. Enhanced Interoperability and Standards: Currently, NFTs are primarily associated with the Ethereum blockchain. However, there is an increasing focus on developing interoperability protocols and standards that allow NFTs to be seamlessly transferred between different blockchain networks. This would enable greater flexibility and liquidity for NFTs and open up new possibilities for cross-chain collaborations and interactions.
4. Sustainable Solutions: One notable concern associated with NFTs is their environmental impact, particularly due to the energy consumption of blockchain networks. In the future, we can expect to see efforts towards developing more sustainable solutions, such as the utilization of energy-efficient blockchains, the adoption of proof-of-stake consensus algorithms, or the exploration of layer-two scaling solutions. These advancements would address the environmental concerns and contribute to the long-term viability of NFTs.
5. Improved User Experience and Accessibility: As NFT adoption continues to grow, there will likely be a focus on enhancing the user experience and making NFTs more accessible to a broader audience. User-friendly platforms and marketplaces with intuitive interfaces, simplified onboarding processes, and improved transaction efficiency are expected to emerge. This would encourage broader participation and make it easier for both creators and collectors to engage with NFTs.
6. Integration of DeFi and NFTs: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has gained significant attention in the blockchain space. The integration of DeFi with NFTs presents exciting possibilities, such as leveraging NFTs as collateral for loans, fractional ownership of NFTs through tokenization, or the creation of NFT-based financial products and derivatives. The convergence of DeFi and NFTs could unlock new financial opportunities and liquidity for digital assets.
7. Regulation and Legal Frameworks: As NFTs continue to gain prominence, regulatory bodies and governments may develop frameworks to address legal and compliance considerations. This could include regulations related to intellectual property rights, consumer protection, taxation, anti-money laundering (AML), and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. Clearer regulatory guidelines would provide a more stable and secure environment for the growth of the NFT market.
8. Enhanced Social and Community Interactions: NFTs have the potential to transform social interactions and community engagement. They can facilitate new forms of interaction between creators and their fans, allowing for exclusive content, rewards, and collaborations. Additionally, communities could form around shared interests in specific NFT projects or collections, fostering deeper engagement, and creating opportunities for social and economic interactions.
It’s important to note that the future of NFTs will be shaped by various factors, including technological advancements, market dynamics, regulatory developments, and user adoption. While the possibilities are vast, it will be crucial to navigate the challenges and ensure sustainable growth to unlock the full potential of NFTs in the years to come.



























































